
650,000 Children in 9 States Attend School Within 1 Mile of a Fracking Well

More than 650,000 kindergarten through 12th grade children in nine states attend school within one mile of a fracked oil or gas well, putting them at increased risk of health impacts from dangerous chemicals and air pollution.

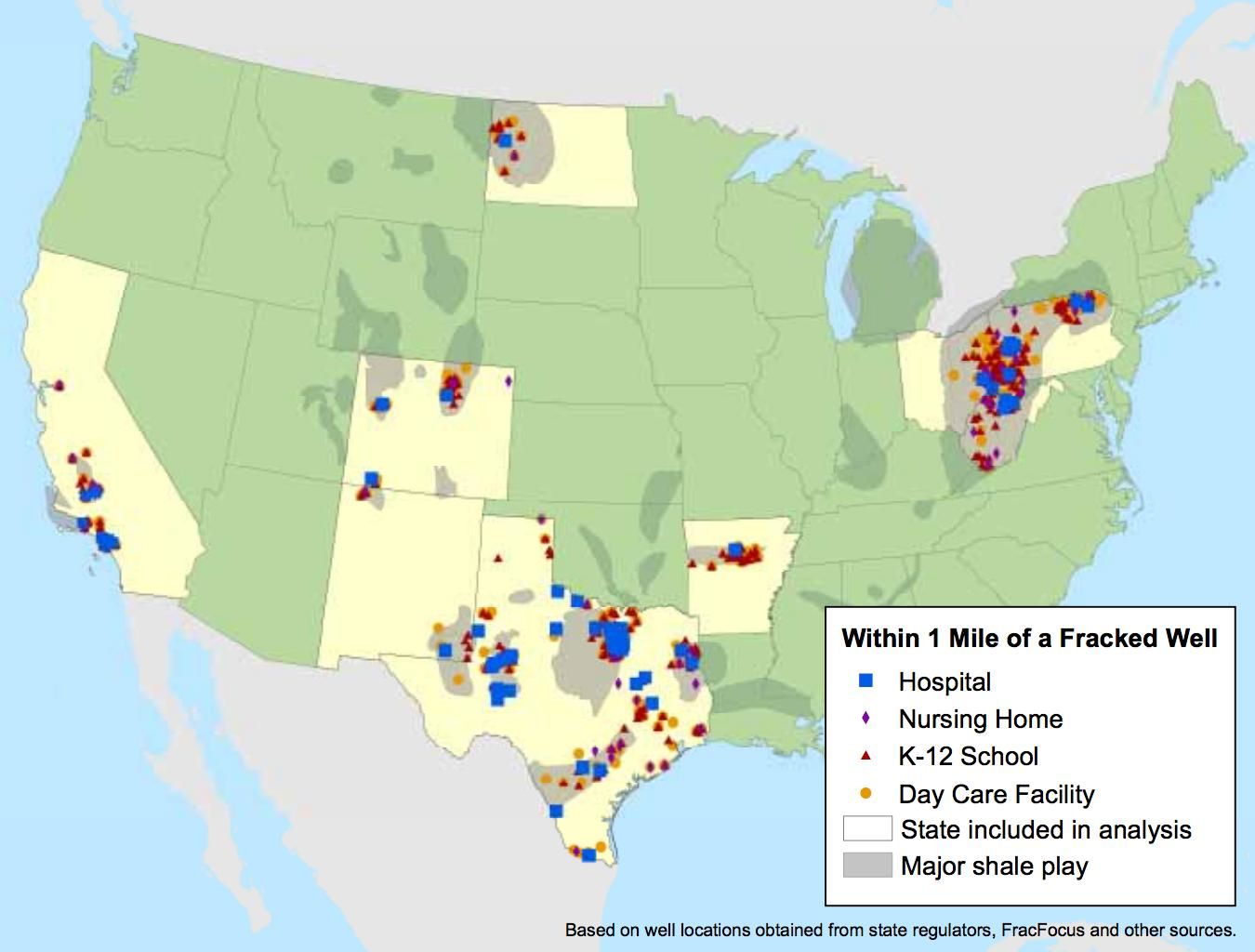
The finding comes from a new study by Environment America Research & Policy Center that exposes the proximity of fracking near schools, hospitals, day care centers and nursing homes, risking the health of our children and other vulnerable populations.
“Schools and day care centers should be safe places for kids to play and learn,” said Rachel Richardson, director of Environment America’s Stop Drilling program and co-author of the report. “Unfortunately, our research shows far too many kids may be exposed to dirty air and toxic chemicals from fracking right next door.”
Using data provided by the oil and gas industry and state regulators, Dangerous and Close—Fracking Puts the Nation’s Most Vulnerable People at Risk, found that:
- 1,947 child care facilities, 1,376 schools, 236 nursing care providers and 103 hospitals are within a one-mile radius of fracked wells in the nine states examined.
- More than 650,000 kindergarten through 12th grade children attend school within one mile of a fracked well.
- The highest percentage of children attending school close to fracked wells is in West Virginia, where 8 percent of children spend their school days within one mile of a fracked well.
- Texas has the largest number of children attending school close to a well, with 437,000 kindergarten through 12th grade students attending public or private school within one mile of a fracked well.
The report included data from nine states total including Arkansas, California, Colorado, New Mexico, North Dakota, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Texas and West Virginia.
“American society aspires to protect children, the sick and the elderly,” said Elizabeth Ridlington, policy analyst with Frontier Group and co-author of the report. “This report shows that we’re violating that ideal because of our overwhelming dependence on fossil fuels. We’ve sunk to putting vulnerable populations at risk instead of making the wholesale shift to conservation and renewable energy.”
Fracking creates a range of threats to our health, including creating toxic air pollution that can reduce lung function even among healthy people, trigger asthma attacks and has been linked to premature death. Children and the elderly are especially vulnerable to fracking’s health risks. Children’s immune systems are more susceptible to damage from toxic chemicals while older adults have weaker immune systems and more difficulty breaking down toxics chemicals in the body.
New Fracking Study Finds Children at Greater Risk of Respiratory Health Problems https://t.co/9khQK6xBHn @POTUS @GovernorTomWolf @EcoWatch
— Frack Action (@FrackAction) May 12, 2016
Studies show that the closer you are to fracking, the more susceptible you are to suffering negative health effects. In Colorado, residents living within one-half mile of fracked wells were exposed to pollutants that increased their risk of illness. Researchers at University of Pennsylvania and Columbia University found that in Pennsylvania hospitalizations rates increase near fracking sites.
Health Dangers of #Fracking Revealed in Johns Hopkins Study https://t.co/XN2bg4eVhO @foodandwater @MarkRuffalo @JoshFoxFilm @ssteingraber1
— EcoWatch (@EcoWatch) August 25, 2016
“Fracking is an inherently dangerous threat to public health and should not be where vulnerable children and families live,” said Dr. Walter Tsou, president of Philadelphia Physicians for Social Responsibility.
“It is an unavoidable fact that as fracking operations have spread across the U.S., significant damage to our health and our environment has occurred,” said Laura Burns, parent of two and field organizer for Mom’s Clean Air Force in Ohio. “Our children are our future. And for the sake of our future, we need to be seeking clean, renewable energy solutions.”
Given the scale and severity of fracking’s impacts, fracking should be prohibited wherever possible and existing wells should be shut down beginning with those near institutions that serve our most vulnerable populations.
To better protect communities already on the front lines of drilling, stricter regulations should be adopted and federal fracking loopholes should be closed to hold the oil and gas industry to the same standards as other industry. Currently, oil and gas companies are exempt from key provisions in the Safe Drinking Water Act, the Clean Air Act, the Clean Water Act, and the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act.
“Our children’s health and safety should be non-negotiable,” Richardson said. “Ultimately, the only solution to this toxic health threat is to ban fracking entirely and move toward 100 percent renewable energy as swiftly as possible.”

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 