

Europe ranks second only behind Asia in terms of e-waste, according to the Platform for Accelerating the Circular Economy. Ladislav Kubeš / iStock / Getty Images Plus
By Tim Schauenberg
Technician Christopher Olk concentrates hard as he removes the broken drive from a DVD player and pushes it back in again.
“If it’s the mechanics or the electronics, I can fix it,” explains the 26-year-old, who is working on his Ph.D. in battery technology at Aachen University. “If the chip or the cooling system is affected then I can’t do anything, because I’m missing the equipment and spare parts.”
In a small room inside a repair cafe in Cologne’s civic center, Olk is one of four technicians who, with the help of some spanners and a soldering iron, try to breathe new life into faulty electronic devices, whether it’s a razor, a toaster, a screen or a lamp.
Europe is full of broken-down equipment. With more than 12 million tons per year — the equivalent of 30,000 jumbo jets — Europe ranks second only behind Asia in terms of e-waste, according to the Platform for Accelerating the Circular Economy (PACE).
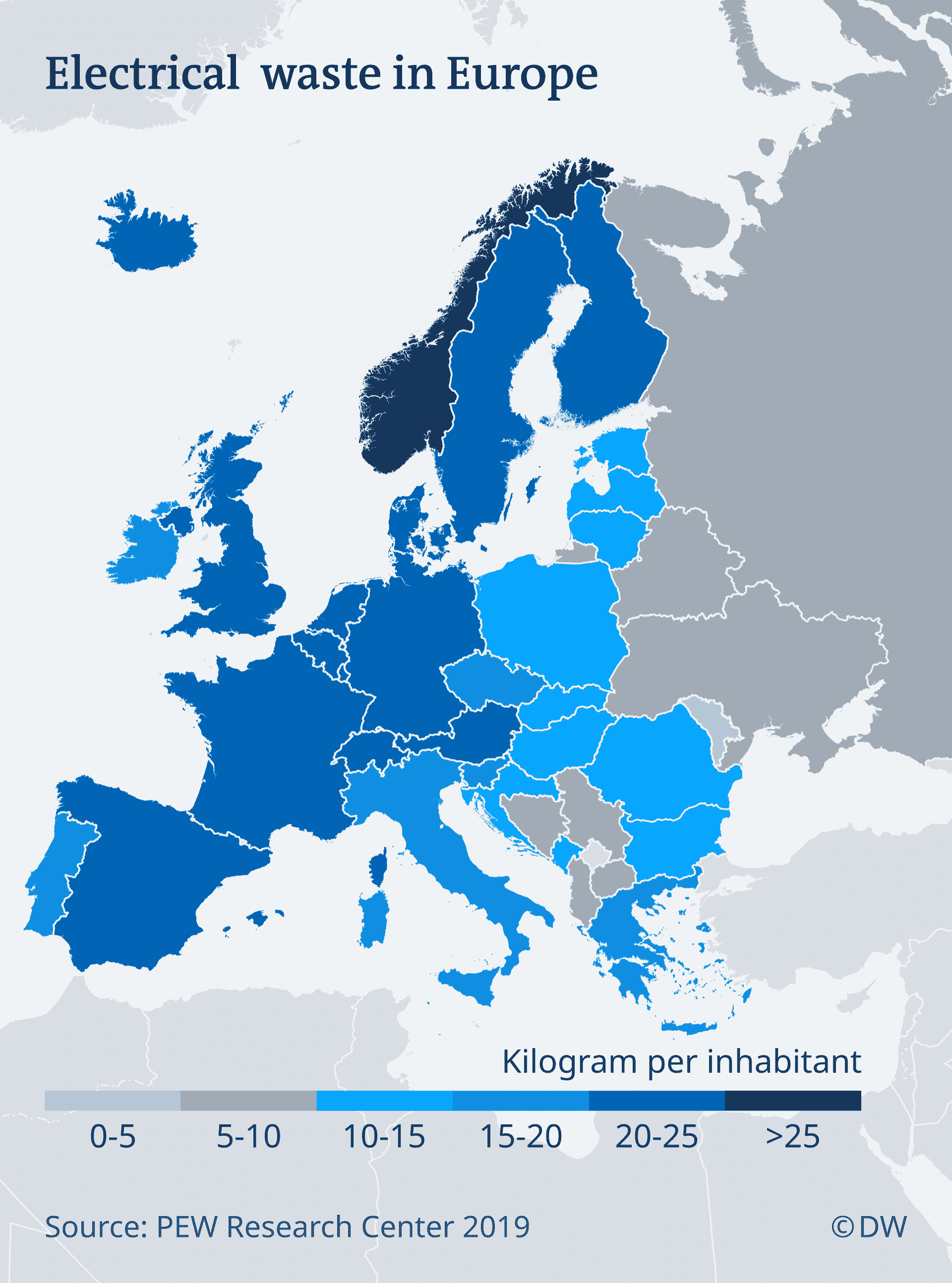
Manufacturers to Make Changes
“We want to avoid electronic waste and try to motivate people to act in an environmentally conscious way,” says Dunja Karabaic, one of the repair cafe’s founders.
The European Commission now wants to implement a new ecodesign directive at the EU level to help ensure home appliances have a longer functional lifespan — and it’s banking on regulation.

At the repair cafe in Cologne, Christopher Olk is trying to get this faulty DVD player up and running again.
As of 2021, manufacturers across Europe will be required to improve both the reparability and service life of devices such as washing machines, refrigerators, dishwashers, electric motors, light sources and LED screens. Manufacturers must also be more precise when it comes to including energy consumption information on the labels of their products and providing replacement parts for at least 10 years after purchase.
Laptops and smartphones, however, are not covered under the new rules — more on that later.
Ecological Potential and the Right to Repair
The European Commission estimates that up to 167 terawatt hours of energy could be saved annually by 2030 — approximately the same annual energy consumption as Denmark, which has a population of 5.8 million. This could be achieved, on the one hand, through more energy efficient devices, and, on the other, as a result of fewer devices needing to be re-produced if they last longer in the first place.
When it comes to electricity and acquisition prices, the European Commission projects that EU citizens would save around €150 (7) per year in the future.

Old televisions are much easier to repair compared to modern LED screens.
“Whether it is by fostering reparability or improving water consumption, intelligent ecodesign makes us use our resources more efficiently, bringing clear economic and environmental benefits,” the European Commission Vice President for Jobs, Growth, Investment and Competitiveness, Jyrki Katainen, said in an official statement.
Environmental organizations have also welcomed the new regulations.
“From the U.S. to Europe, people are demanding their right to repair things they own because they’re tired of products that are designed to break prematurely,” said Chloe Fayole, the program and strategy director at the environmental organization ECOS. “Enabling consumers to repair and reuse all electronic products is just common sense.”
How Long Should Devices Last?
Exactly how much longer electronic devices should last in the future is still unclear, as is a more detailed benefit analysis of the plan. But if the devices are easier to repair, “the turnover of product inventories will automatically decrease,” Pierre Schweitzer, an expert on ecodesign at the European Environment Bureau (EEB) told DW. “That means that less electronic waste will be produced. But no one has tested the model yet, as to whether this will happen in practice.”
The EEB has therefore submitted a report looking at the effects of measures which prolong the life of electronic devices. The calculations show that if washing machines in Europe were to function for just one extra year, it would have the same positive effect on the environment as if 133,000 cars were taken off the road.
On average, a washing machine currently lasts around 11 years. But according to the experts, it would have to be used for at least 20 years before the purchase of a new washing machine is advisable from an environmental point of view.
“That’s how long it takes resources to use an old device — and to repair it,” explains Rasmus Priess, a product sustainability expert from the Öko-Institut in Freiburg.
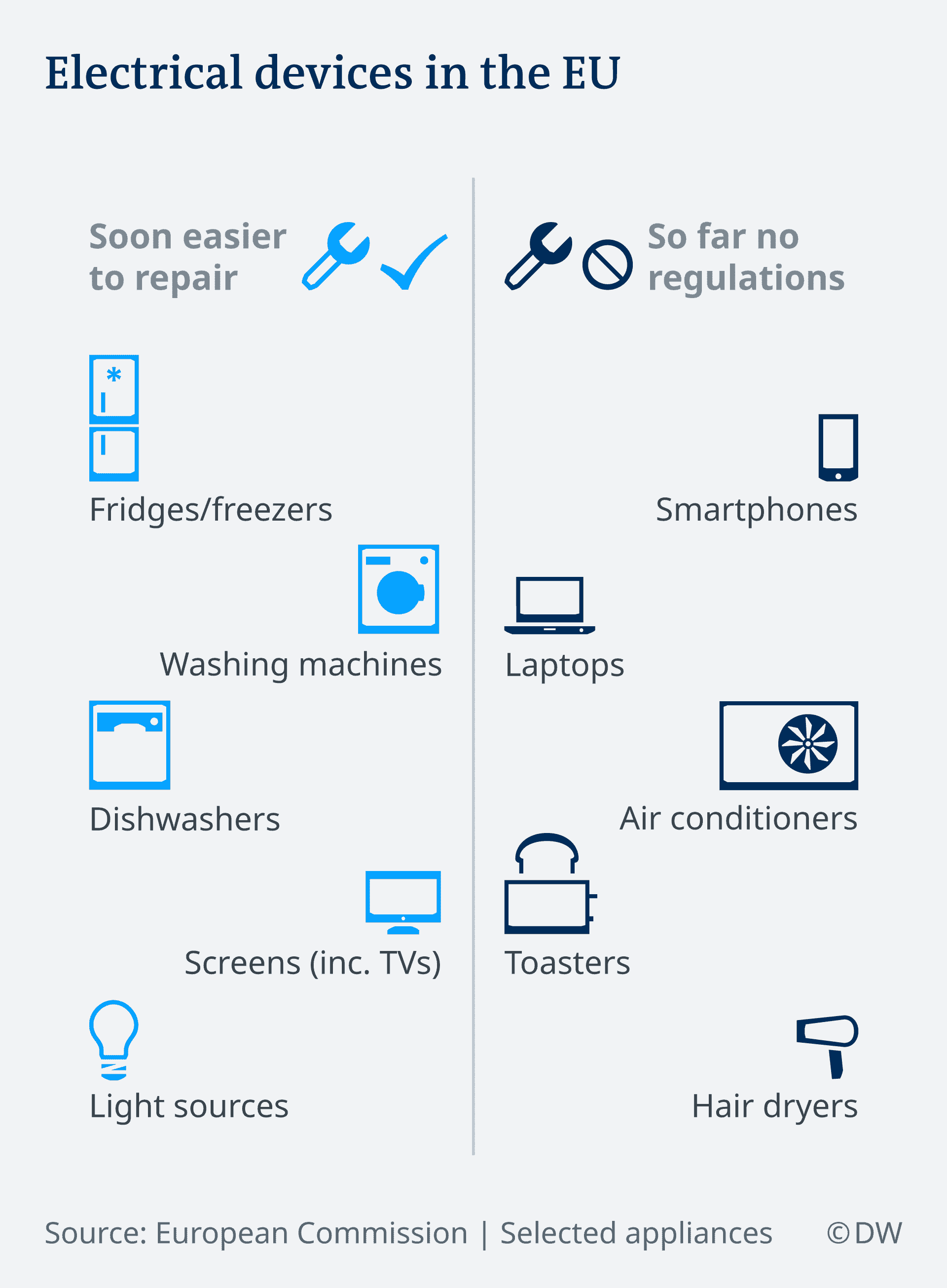
But not all electronic devices are created equal. If the energy footprint required to manufacture and then run a device is taken into account, a laptop should be used for 44 years, and a smartphone for up to 232 years. As mentioned earlier, these devices – along with small appliances like razors, blenders and toasters – won’t be included in the new EU rules. The plan is to incorporate them at a later stage.
The DVD player, which Christopher Olk is busy fixing in the repair café in Cologne, hasn’t made it onto the European Commission’s list yet either.

Brussels will soon be discussing whether to include longer-lasting smartphones and laptops in the new regulations.
Gaps in the Rules
It took Olk 30 minutes to remove the device’s case and take a look inside. After some tinkering, he still only managed open it by force. “See that old radio over there,” he said, pointing to an antique mustard yellow transistor radio that has probably been around for several decades, “Underneath is a guide on how to open it and remove some of the parts. Something like that alone would help.”
The German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Technology (BMWI) has also been negotiating in Brussels. In a statement provided to DW, it says it is committed to ensuring that customers can make simple repairs themselves, while more difficult or dangerous repairs should be done by a specialist.
The cost of replacement parts may also limit the overall success of the new regulations: The scheme doesn’t include a price break for spare parts.
Jean-Pierre Schweitzer from the EEB believes this has increased the risk of “an economic incentive to make spare parts either very expensive, or to manufacture products that break down regularly.”

The more complicated the technology, the harder it is to identify which parts are broken.
An analysis by the Joint Research Center of the European Commission found that the main reason people didn’t have a washing machine or dishwasher repaired was because “it was too expensive.”
Paolo Falcioni, the Director General of APPLiA, an association representing home appliance manufacturers in Europe, has nevertheless praised the regulations as “a balanced representation of interests.” But he also sees some disadvantages. On the one hand, APPLiA fears that the regulations would mean fewer devices would be approved for the European market. On the other hand, it also wants to avoid any unfair competition.
‘Repairing Is More Important Than Recycling’
But although there is still room for improvement, Jean Pierre Schweizer from EEB says the new legislation is “groundbreaking” because it acknowledges the importance of using devices as long as possible.
“When we talk about a circular economy, repairing is a very efficient point at which you can save real resources and emissions — and that’s just the start. We really should highlight the positive aspects of this legislation.”

Not all electronic devices can be repaired using normal, everyday tools.
Back at the repair cafe, Christopher Olk has given up. The DVD player is beyond saving. This isn’t an unusual outcome here.
Braco Sladakovic, who brought in his defective LED TV, has also admitted defeat. The backlight no longer works.
“We tried, but it was too complicated,” he told DW. “It’s not worth it anymore, unfortunately.” The spare part needed is cheap enough to replace, but the repair itself would be too difficult and expensive.
Sladakovic now needs to decide what to do with his broken TV. He might be able to sell if to a hobbyist for a few euros. Or he’ll simply take it to the nearest electronic waste dump.
Reposted with permission from DW.
- 'Right to Repair': Fixing Our Own Broken Stuff Should Be Standard ...
- Dangerous Chemicals From E-Waste Found in Black Plastics From ...
- Thailand to Ban Imports of Plastics and E-Waste - EcoWatch
- Should You Rent, Not Buy, Electronics? - EcoWatch

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 