

PxHere
By Ben Lilliston
New data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) shows a steady increase in agriculture-related greenhouse gas emissions, much of it linked to industrial systems of crop production and the rise of factory farm systems of animal production. The annually updated GHG data is designed to track U.S. emissions related to the Paris Climate Agreement and to inform national and state-level climate policy.
The EPA’s Inventory of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2017 charts GHG emissions both by type and by sector using formats and methodologies established through the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Total U.S. GHG emissions have increased just 1.6 percent since 1990 (with emissions decreasing slightly in recent years), at least partially due to cuts in coal production and growth in renewable energy use. Despite these modest declines, the U.S. is off track to reach its Paris climate commitments, and according to Climate Action Tracker, a series of Trump administration regulatory rollbacks threaten to slow progress further.
While emissions in many sectors are declining, those from the agriculture sector have increased more than 10 percent since 1990, according to the EPA. The agency found that agriculture accounted for 8.4 percent of U.S. emissions in 2017. That percentage does not include on-farm energy and fuel use (counted in the energy section of the inventory), nor does it count emissions related to shifts in cropland (counted in the Land Use, Land Use Change and Forestry section), the production of ammonia fertilizer (included in the Industrial Processes section of the report), nor other elements of the food system related to transport, processing and waste.
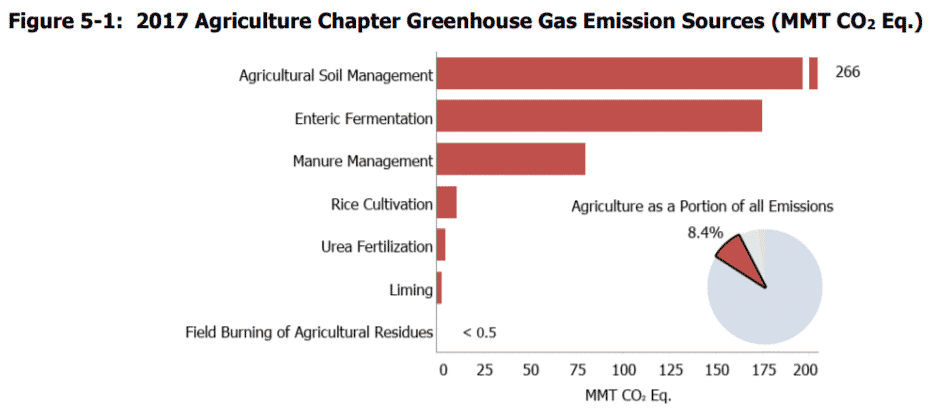
Via EPA Draft Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks 1990-2017
Within the agriculture sector, carbon dioxide emissions increased by 16.2 percent, methane emissions by 14.4 percent and nitrous oxide emissions by 7.3 percent since 1990, the EPA reported. Methane is 28 times as potent as carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide is nearly 300 times as potent.
The increase in methane emissions mirrors the rapid expansion of factory farms in the U.S. over the last two decades, where thousands of animals are raised in confined spaces and include massive manure lagoons. Ruminant animals like cattle are the major source of agricultural methane emissions because of their unique digestive systems. Enteric fermentation emissions, primarily from beef and dairy cattle, have risen 6.9 percent since 1990. “This increase in [methane] emissions from 1990 to 2017 generally follows the increasing trends in cattle populations,” found the EPA.
Emissions related to manure management rose 66 percent since 1990. The EPA reported, “The majority of this increase is due to swine and dairy cow manure, where emissions increased 29 and 134 percent, respectively.” The EPA pointed out that “the shift toward larger dairy cattle and swine facilities since 1990 has translated into an increasing use of liquid manure management systems, which have higher potential CH4 (methane) emissions than dry systems.”
Manure management is also a source of nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions, both directly and through the application of manure on fields as fertilizer. N2O emissions related to manure increased 34 percent from 1990 to 2017 — once again mostly associated with the rise of large-scale operations, which produce massive amounts of concentrated waste that is often over-applied as fertilizer.
Nitrous oxide emissions related to agricultural soil management, including synthetic fertilizer application and tillage practices, increased by six percent from 1990. The increase in the use of synthetic fertilizers explains part of the increase. The EPA reported, “Direct N2O emissions from croplands occur throughout all of the cropland regions but tend to be high in the Midwestern Corn Belt Region (Illinois, Iowa, Indiana, Ohio, southern Minnesota and Wisconsin, and eastern Nebraska), where a large portion of the land is used for growing highly fertilized corn and N-fixing soybean crops.”
The EPA also noted a 109 percent increase in carbon dioxide emissions related to the application of urea fertilizer, a form of synthetic nitrogen fertilizer. And, the EPA’s land use chapter documented the loss of more than 10 million hectares of cropland since 1990, largely due to development. This decrease in cropland resulted in a loss in the rate of carbon storage of about 44 percent since 1990. “This decline is largely due to lower sequestration rates and less annual cropland enrolled in the CRP (the set aside Conservation Reserve Program),” said the report.
A noticeable gap in the data is the evaluation of diverse types of farming systems, including agroecological systems which incorporate more types of crop rotations and soil health-building practices like the use of perennials or cover crops. Systems focused on building soil health can better withstand weather extremes like intense rains or drought, according to the USDA. Recent research indicates that regenerative organic systems, and sustainably managed, pasture-based systems can actually sequester more GHGs than they produce.
The methodology for tracking GHG emissions is evolving, and this is particularly true for the agriculture sector where farming systems can result in dramatically different emission levels. The latest EPA data indicate that the increases in agriculture GHGs are linked primarily to the expansion of industrial systems of production for crops and animals. As policymakers develop future climate policy, it will be critical that they differentiate between industrial, factory farm systems and regenerative systems of production that can help respond to climate change.
Reposted with permission from our media associate Common Dreams.

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 