

While your home may feel like the safest place you could be, the air may contain a number of indoor air pollutants that can cause respiratory problems like asthma, or even diseases like lung cancer.
Here are six of the most common air pollutants found in homes and ways to reduce or eliminate them.
1. Dust Mites
Dust mites are microscopic insects that are commonly found living among humans in bedding, upholstery, mattresses, curtains and carpets. They prefer warm, humid environments and can multiply easily in these conditions. A relative of the spider, dust mites feed on organic detritus, like flakes of human skin. Worldwide, they are a common cause of asthma and allergic rhinitis. Not only is it extremely difficult to see them with the naked eye (an adult mite is about two to four times the diameter of a shaft of human hair), it is difficult to completely rid your home of the ubiquitous mites, but you can reduce their population.
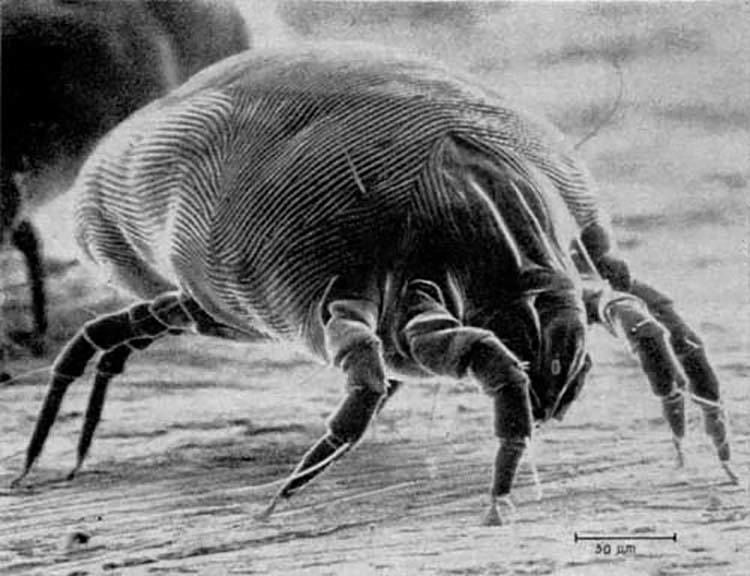

First, try to keep the humidity inside your home to less than 50 percent. Air conditioners and dehumidifiers can help. Protect your bed by covering it with allergen-resistant covers. Make sure you wash your sheets and blankets regularly in hot water. You can also put beddings, removable upholstery and curtains in a hot tumble dryer for 20 minutes to kill them. And don’t give mites a place to hide and breed: keep your home as dust-, dander- and clutter-free as possible. Regular vacuuming is a must.
2. Mold
People have varying sensitivities to mold, a type of fungi that grows in warm, damp, humid environments. Some symptoms from exposure to mold include eye and skin irritation, coughing, wheezing and nasal congestion. Severe reactions include shortness of breath and fever. People with chronic lung illnesses may even develop mold infection in their lungs. Inside your home, the best places to check for mold are damp and moist environments, such as basements, showers, kitchens and houseplants.

To clean up mold, you can use soap and water or a bleach solution of one cup laundry bleach to one gallon of water. If you are using bleach, open windows to make sure fresh air is getting inside and protect yourself by wearing gloves and protective eyewear. Also make sure never to mix bleach with ammonia or other household cleaners, as that will create toxic fumes. When cleaning your bathroom, choose products that contain mold-killing agents. Don’t use carpeting in basements and bathrooms, as it can retain moisture. And don’t keep firewood indoors, as it can harbor mold. Also, check the soil of your houseplants regularly and replant any plants that have mold growing on the soil. But don’t get rid of plants; houseplants can help filter and clean the air.
3. Pet Dander
Pet dander is composed of tiny and even microscopic flecks of skin shed by dogs, cats, rodents, birds and other common pets with fur or feathers that can trigger allergic reactions in some people. According to the American Lung Assocation, about twice as many people report allergies to cats than to dogs.

If you have pets and suspect that you or someone in your home is allergic to dander, keep your pets out of the bedroom. Don’t allow them on upholstered furniture and get rid of rugs or carpeting, which can retain dander. Keep your home clean by regular vacuuming and brush your pet regularly to remove loose dander and bathe them regularly to keep their skin healthy, as healthy skin that is not dry or irritated sheds less dead skin cells. If you’re thinking about getting a dog, consider a smaller dog who will shed less dander. Also, feed your pet high-quality food that has a good balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These oils will help keep your pet’s skin healthy and keep your vet bills down.
4. Radon
Radon is an odorless, tasteless and invisible naturally occurring radioactive gas that is formed by the decay or uranium in rock, soil and water. Once produced, it moves through the ground and into the air. Found in all 50 states, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer worldwide, after smoking. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates approximately 21,000 lung cancer deaths in the U.S. are radon-related. According to the National Safety Council, “Radon gas decays into radioactive particles that can get trapped in your lungs when you breathe. As they break down further, these particles release small bursts of energy. This can damage lung tissue and lead to lung cancer over the course of your lifetime.”
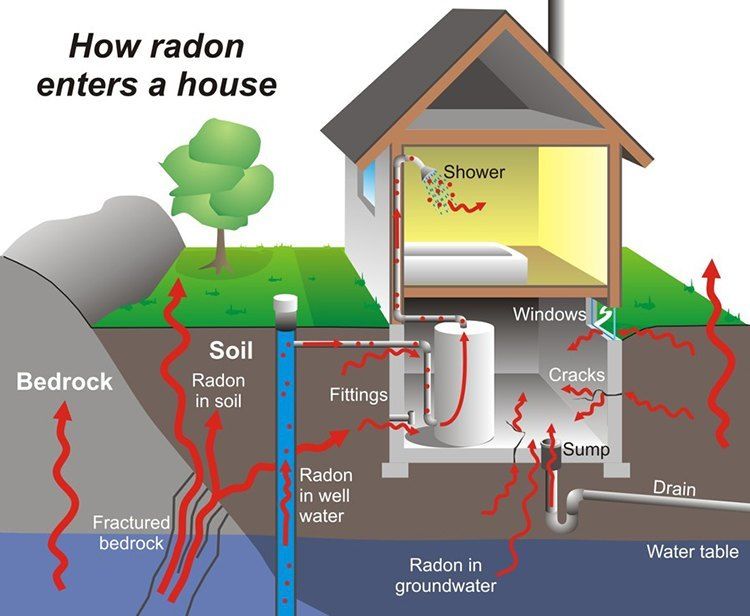
There is an ongoing concern that granite kitchen countertops emit radon at potentially harmful levels. According to the EPA, most of the radon found in indoor air comes from the soil underneath the home.
According to the Kansas State University National Radon Program Services, one out of 15 homes nationally—about six percent—may have elevated indoor radon levels that should be lower. To test your home for radon levels, visit the U.S. EPA website.
5. Smoke
Secondhand smoke from cigarettes is deadly. According to the Centers for Disease Control, tobacco smoke contains more than 7,000 chemicals, including hundreds of toxins, about 70 of which can cause cancer. Secondhand smoke is very harmful to children, who can experience ear infections, more frequent and severe asthma attacks, respiratory infections like bronchitis and pneumonia, and a greater risk of sudden infant death syndrome. It’s bad for adult as well. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, secondhand smoke caused nearly 34,000 heart disease deaths each year from 2005–2009 among adult nonsmokers in the United States.
The only way to fully protect your home from this health hazard is to eliminate smoking in your home. If visitors would like to smoke, ask them to step outside. If you’re a smoker and have children at home, don’t smoke indoors and don’t smoke near them when you’re outside the home.
6. Household Cleaners
Ordinary household cleaners emit a wide array of harmful chemicals, such as chlorine, ammonia, phthalates and triclosan. You can easily avoid exposure to these toxins by avoiding over-the-counter cleaning products. Instead, choose DIY natural non-toxic cleaning solutions, such as lemon, olive oil, white vinegar, baking soda and club soda.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE
Duke Researchers Find Nail Polish Chemical in Women’s Bodies
The People vs. the Koch-Funded Asbestos Industry
Stop Giving Cancer Patients Toxic Cosmetics to ‘Look Good, Feel Better’

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 