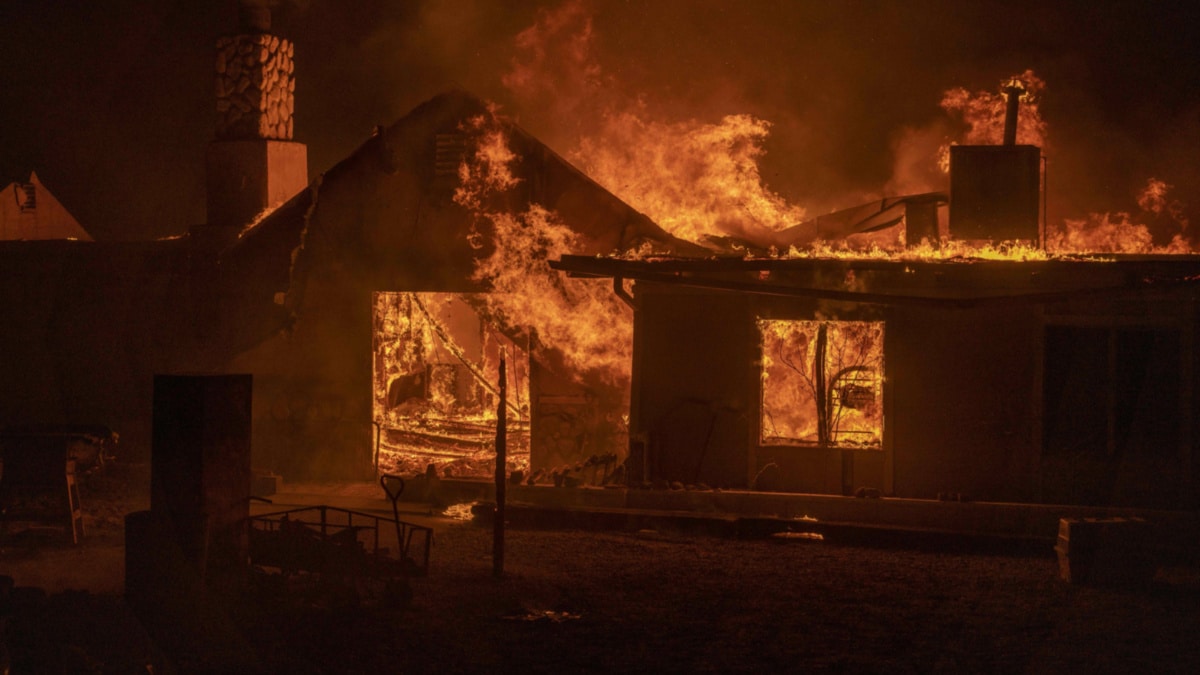


A home burns during the Bobcat Fire in Juniper Hills, California on September 18, 2020. Kyle Grillot / AFP/ Getty Images
By Stuart Braun
“These are not just wildfires, they are climate fires,” Jay Inslee, Governor of Washington State, said as he stood amid the charred remains of the town of Malden west of Seattle earlier this month. “This is not an act of God,” he added. “This has happened because we have changed the climate of the state of Washington in dramatic ways.”
As megafires devastated the entire West Coast of the U.S., Inslee rejected reference to wildfires since the word implies naturally occurring fires.
By contrast, the term climate fires explicitly links record-breaking blazes that have burned across California, Oregon and Washington to global heating caused by the burning of coal, oil and gas.
As California Governor Gavin Newsom inspected the ashen countryside in the county of Oroville in his home state, he doubled down on the source of the fires. “This is a climate damn emergency,” he said.
The pointed link to climate has been partly a response to President’s Donald Trump’s insistence that poor forest management, not climate change, is to blame for the fires. Meanwhile, research shows barely 13% of broadcast news segments about the West Coast fires during their peak mentioned climate change.
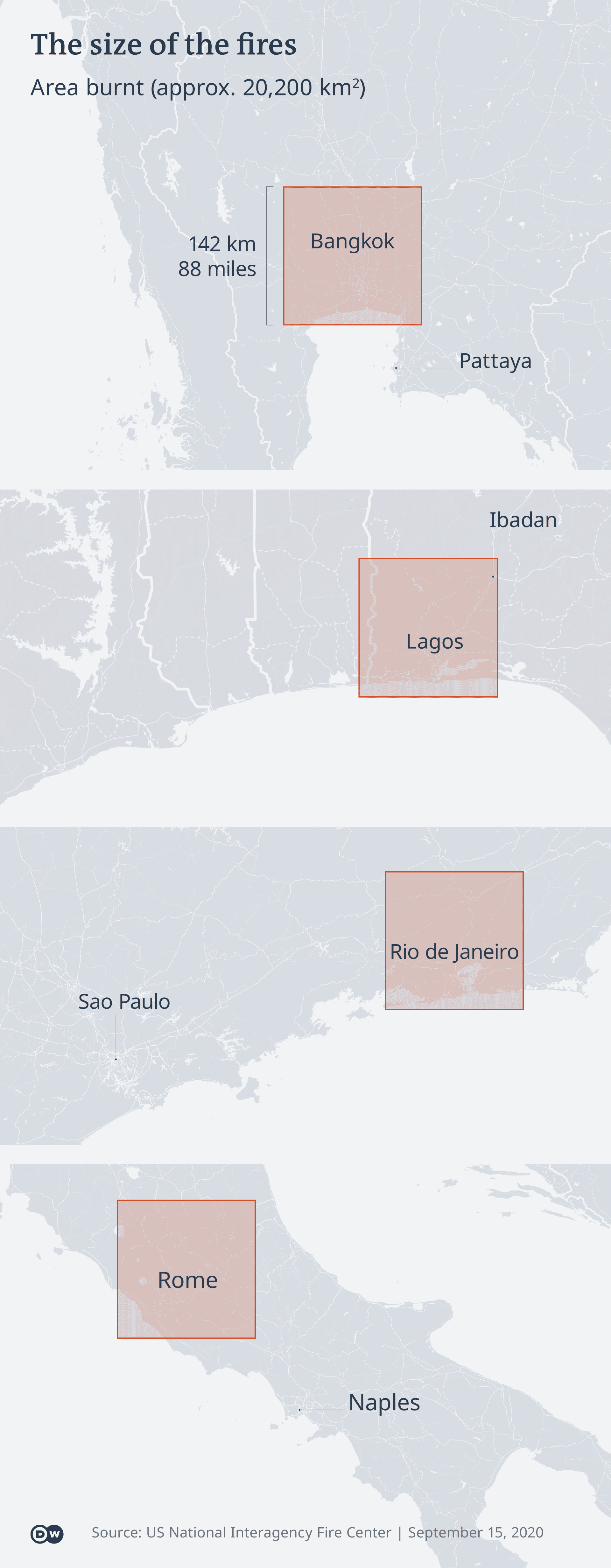
‘These Aren’t Wildfires’
Sam Ricketts, who led climate policy and strategy for Governor Jay Inslee’s 2020 presidential campaign, tweeted on September 11 that “These aren’t wildfires. These are #climatefires, driven by fossil fuel pollution.”
“The rate and the strength and the devastation wrought by these disasters are fueled by climate change,” Ricketts told DW of fires that have burnt well over 5 million acres across California, Oregon, Washington State, and into neighboring Idaho.
In a two-day period in early September, Ricketts notes that more of Washington State burned than in almost any entire fire season until now, apart from 2015.
California, meanwhile, was a tinderbox after its hottest summer on record, with temperatures in Death Valley reaching nearly 130 degrees Fahrenheit, according to the U.S. National Weather Service. It has been reported as the hottest temperature ever measured on Earth.
Drought-parched wetlands in South America have been burning for weeks. https://t.co/pjAKdFcKPg #Pantanal pic.twitter.com/ImN2C5vwcp
— NASA Earth (@NASAEarth) September 18, 2020
As evidenced by Australia’s apocalyptic Black Summer of 2019-2020, fires are burning bigger and for longer, with new records set year-on-year. Right now, Brazil’s vast and highly biodiverse Pantanal wetlands are suffering from catastrophic fires.
#climatefires Started in Australia
Governor Inslee this month invoked the phrase climate fires for arguably the first time in the U.S., according to Ricketts.
But the term was also used as fires burnt out of control in Australia in late 2019. In the face of a 2000km (more than 1,200 miles) fire front, and government officials and media who played down the link to climate change, Greens Party Senator Sarah Hanson-Young and a friend decided that reference to bushfires was inadequate.
“We both just said, we’ve got to start calling them climate fires, that’s what they are,” the Australian Senator told DW.
Hanson-Young says scientists have been warning for decades that these would be the effects of global heating. “We’ve been told these kinds of extreme weather events and destruction is what climate change would look like, and it’s right here on our doorstep,” she said from her home state of South Australia — where by early September fire warnings had already been issued.
“Calling them climate fires was making it absolutely crystal clear. It is essential that there’s no ambiguity,” she said
Having deliberately invoked the term, Hanson-Young soon started to push it on social media via a #climatefires hashtag.
How to Talk About the Urgency of Global Heating
The need to use more explicit language when talking about extreme weather events linked to climate change is part of a broader push to express the urgency of global heating. In 2019, activist Greta Thunberg tweeted that the term “climate change” did not reflect the seriousness of the situation.
“Can we all now please stop saying ‘climate change’ and instead call it what it is: climate breakdown, climate crisis, climate emergency, ecological breakdown, ecological crisis and ecological emergency?” she wrote.
“Climate change has for a long time been talked about as something that is a danger in the future,” said Hansen-Young. “But the consequences are already here. When people hear the word crisis, they understand that something has to happen, that action has to be taken.”
Some terms are now used in public policy, with state and national governments, and indeed the EU Parliament, declaring an official climate emergency in the last year.
Words That Reflect the Science
But while the West Coast governors all fervently link the fires to an unfolding climate crisis, U.S. President Donald Trump continues to avoid any reference to climate. In a briefing about the fires, he responded to overtures by Wade Crowfoot, California’s Natural Resources Secretary, to work with the states on the climate crisis by stating: “It’ll start getting cooler. You just watch.” Crowfoot replied by saying that scientists disagreed. Trump rejoined with “I don’t think science knows, actually.”
It was reminiscent of the anti-science approach to the coronavirus pandemic within the Trump administration, at least publicly. Fossil fuel companies are also benefiting from his disavowal of climate science, with the Trump administration having pulled out of the Paris Agreement and reopened fossil fuel infrastructure like the Keystone XL pipeline.
But the science community has responded, with Scientific American magazine endorsing Trump’s Democratic presidential challenger Joe Biden, the first presidential endorsement in its 175-year history.
Hanson-Young says the use of explicit language like climate fires has also been important in Australia due to the climate denialism of politicians and the press, especially in publications owned by Rupert Murdoch. As fires burnt out much of Australia’s southeast coast, they were commonly blamed on arson — a tactic also recently used in the U.S.
Climate Rhetoric Could Help Decide Election
The language of climate has begun to influence the U.S. presidential election campaign, with Democratic nominee Joe Biden labelling President Trump a “climate arsonist.”
Biden is touting a robust climate plan that includes a 2050 zero emissions target and a return to the Paris Agreement. Though lacking the ambition of The New Green Deal, it has been front and center of his policy platform in recent days, at a time when five hurricanes are battering the U.S. Gulf Coast while smoke blanketing the West Coast spreads all the way to the East.
People are experiencing the climate crisis in a visceral way and almost universally relate to the language of an emergency, says Ricketts. “They know something is wrong.”
Reposted with permission from Deutsche Welle.
- The Vicious Climate-Wildfire Cycle - EcoWatch
- How Climate Change Ignites Wildfires From California to South Africa
- 31 Dead, 250,000 Evacuated in California Fires as Governor ...

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 