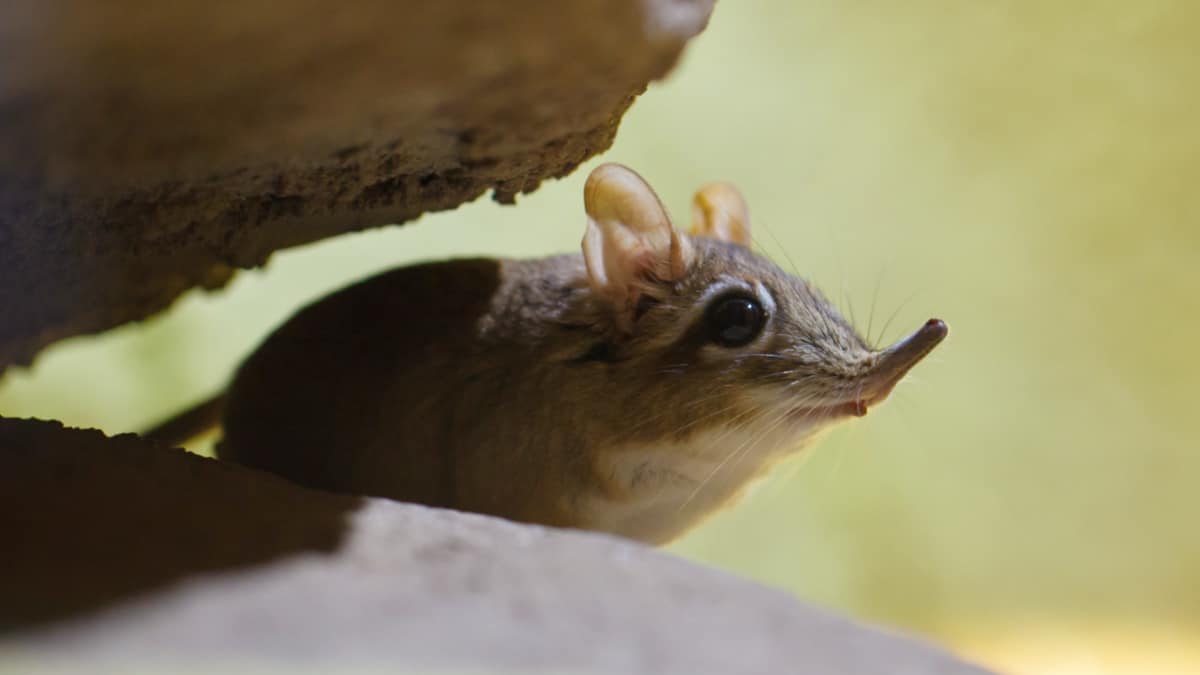


Here are five examples of what are often referred to as Lazarus species – breeds that have seemingly come back from the dead, like this elephant shrew. Petr Kratochvil / Needpix
By Sean Fleming
As many as one million species of animal and plant could face extinction. This dramatic decline in the health of global biodiversity is a crisis in itself as well as a threat to the wellbeing of the planet’s population, the UN warns. Plus, it poses a very immediate risk to global food security and economic activity.
Since the 16th century, hundreds of species of vertebrates have disappeared – almost all due to human-related changes such as loss of habitat or over-hunting. That threat remains present with around 40% of amphibians, 33% of marine mammals and 14% of birds all facing an uncertain future.
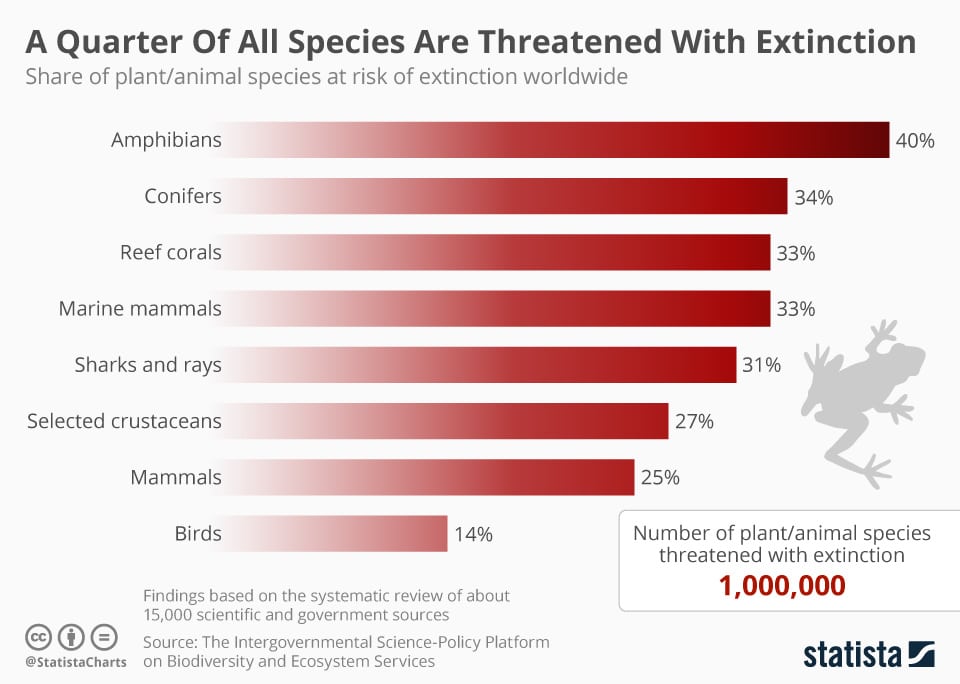
A quarter of all species are threatened with extinction. Statista
That said, there have been many notable conservation successes. There have also been several discoveries of animals that were believed to have become extinct. Here are five examples of what are often referred to as Lazarus species – breeds that have seemingly come back from the dead.
1. Elephant Shrew
The last time anyone recorded a sighting of the Somali elephant shrew was almost 50 years ago, after which, it was assumed to have become extinct. Then, in August 2020, a team of researchers and academics reported that these tiny, odd-looking creatures were alive and well. Also known as the Somali Sengi, this mouse-sized animal, with its distinctive elongated nose, is thriving across the Horn of Africa.
2. Terror Skink
In 1872, the French botanist Benjamin Balansa noted the discovery of a lizard while visiting the French Pacific territory of New Caledonia. At around 50cm (20 inches) in length, it probably wasn’t too hard to spot. Yet, the terror skink – the ‘terror’ part of the name refers to its mouthful of rapacious teeth – was never seen again. Not until 2003, that is. Having been rediscovered by scientists, more research is now underway to learn more about them.
3. Cuban Solenodon
There are few venomous mammals in the world – the Cuban solenodon is one such example. But it was a missing example for some time. Although never technically extinct, its numbers are so low and sightings are so rare, that it has often been thought to be. The Cuban solenodon’s forebears were around at the same time as dinosaurs: it is “a ‘living fossil’ that hasn’t changed much in millions of years,” according to the publication Scientific American. Its bite can kill yet it lacks the strength and dexterity to defend itself or flee from danger, making it an easy target for predators. Deforestation has also contributed to population disturbance.
4. Bermuda Petrel
The Cahow, or Bermuda petrel, was last seen on Nonsuch Island in 1620. But here in 2020, you can watch webcam footage of them. A small number of the birds were spotted nesting in the east of Bermuda in the 1950s, and the population has since been resurrected. The Cahow is a burrowing bird and much of its natural habitat has been destroyed by sea erosion and hurricane damage. New nesting sites were constructed by the Government of Bermuda, while chicks from established populations were relocated to Nonsuch, too.
5. Australian Night Parrot
Another elusive bird, the Australian night parrot, was thought to be extinct after the last recorded sighting in 1912. Then, in 1990, one was found in the state of Queensland. Sadly, it was dead. It would be another 23 years before a living example was spotted by a researcher. The precise location of that sighting was kept secret to protect the birds, whose populations are now closely monitored and who live in vast wildlife sanctuaries.
Reposted with permission from World Economic Forum.
- Koalas Face Extinction in Next 30 Years Without Urgent Intervention ...
- Biggest Animals Face Extinction Due to Hunting - EcoWatch
- De-Extinction: If We Could Revive a Species, Does It Mean We ...
- Giant ‘Toothed’ Birds Flew Over Antarctica 40 Million Years Ago - EcoWatch
- Giant ‘Toothed’ Birds Flew Over Antarctica 40 Million Years Ago - EcoWatch
- What We’ve Lost: The Species Declared Extinct in 2020 - EcoWatch
- ‘Living Fossil’ Rediscovered off Japan’s Coast

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 