By U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service
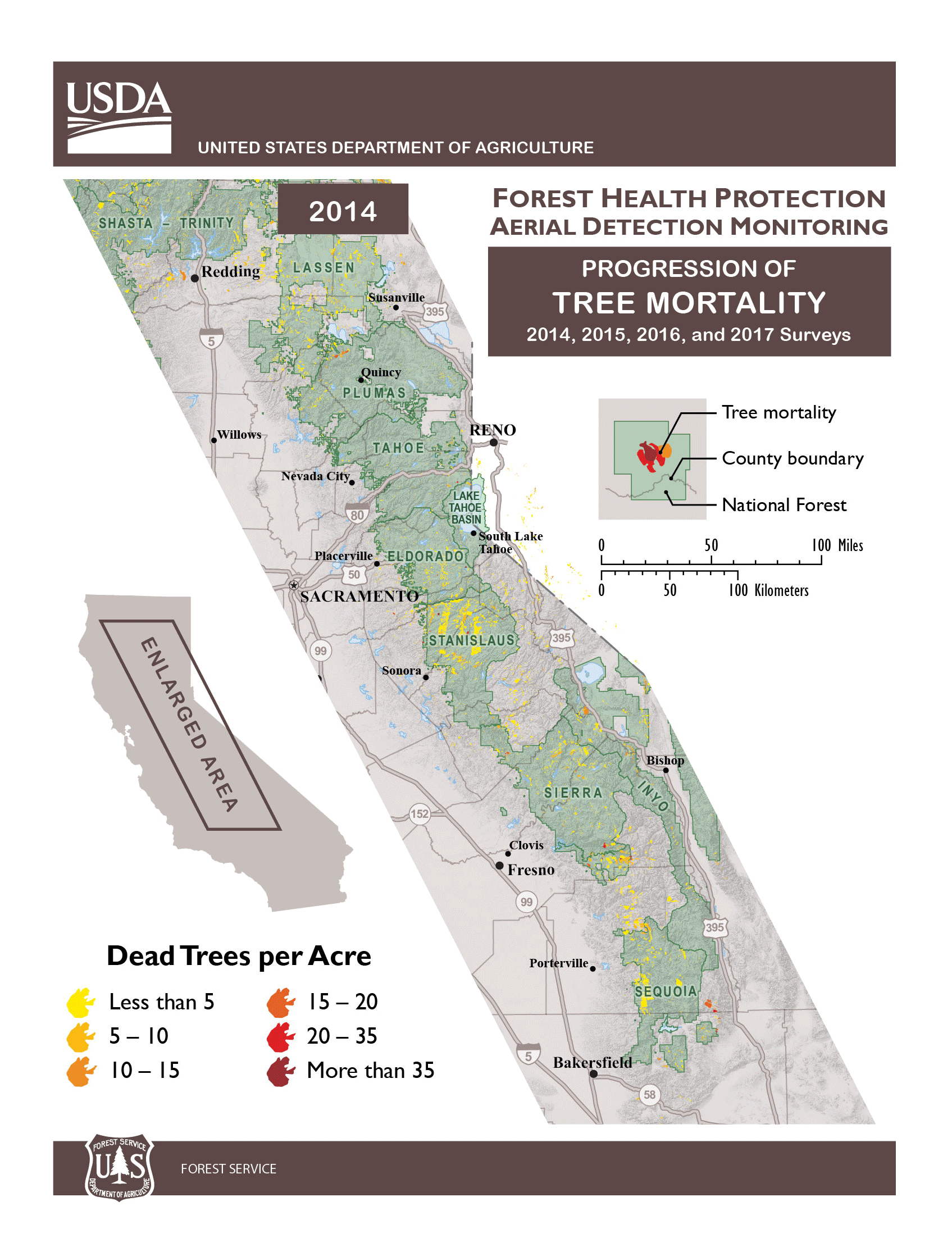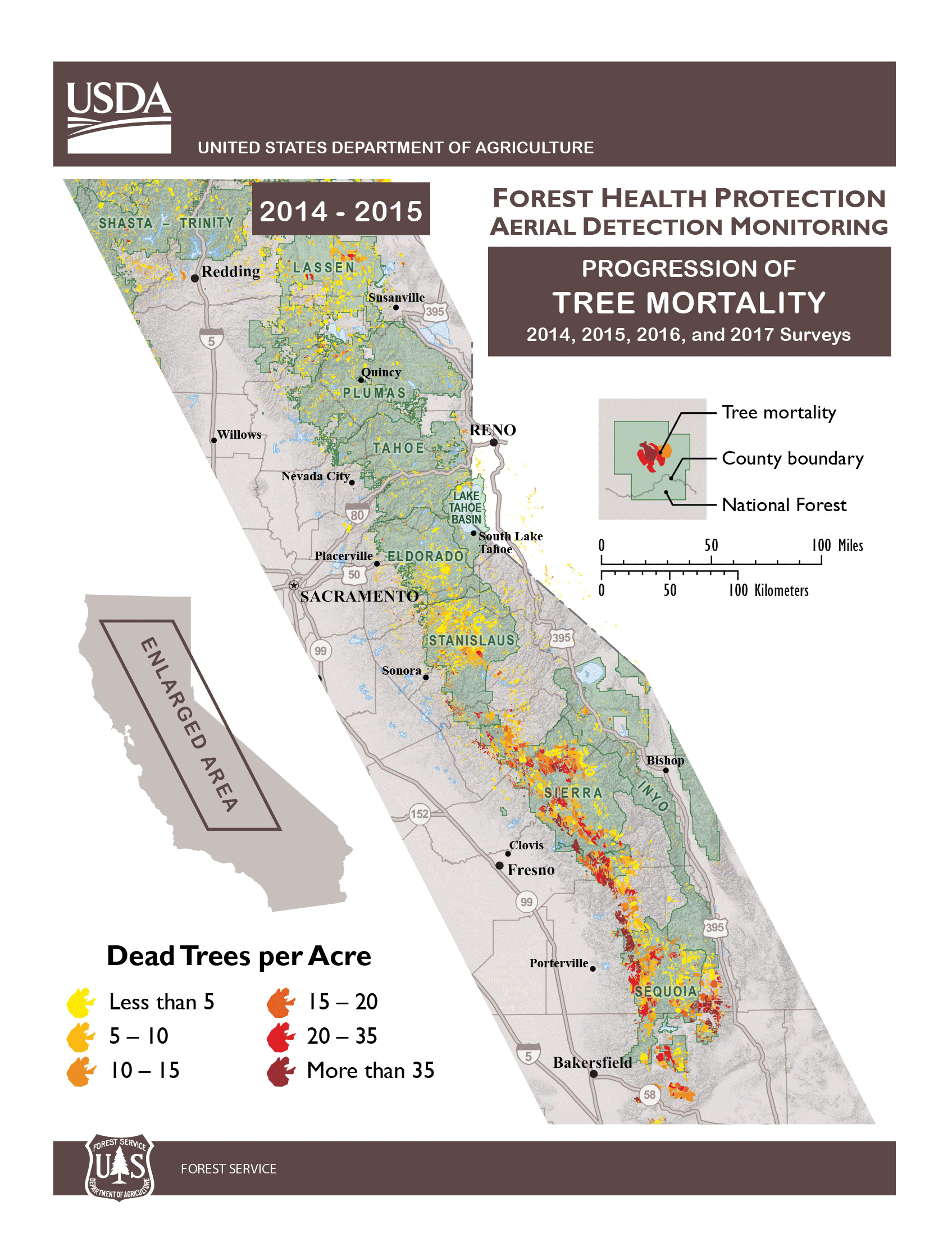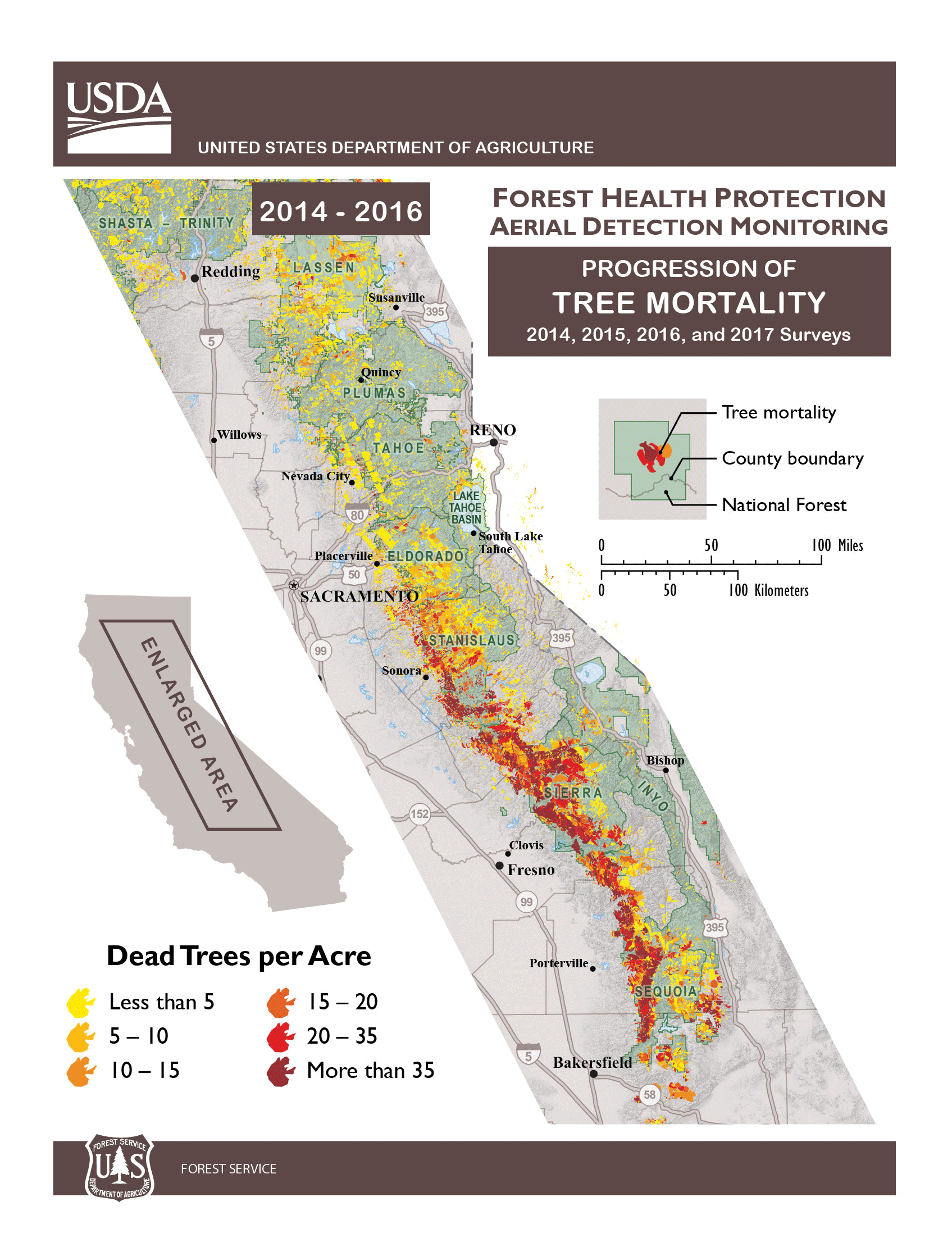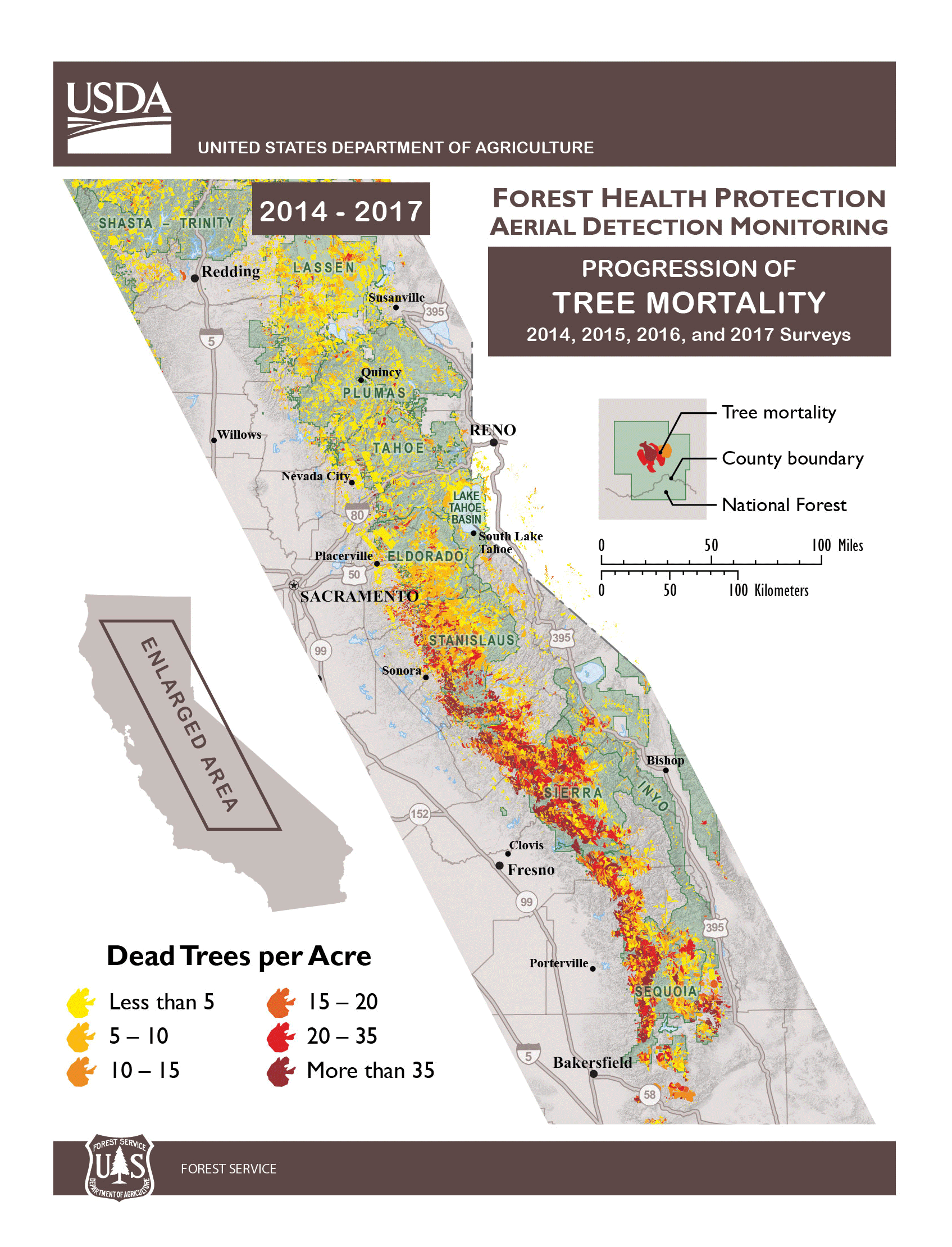
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Forest Service Monday announced that an additional 27 million trees, mostly conifers, died throughout California since November 2016, bringing the total number of trees that have died due to drought and bark beetles to an historic 129 million on 8.9 million acres. The dead trees continue to pose a hazard to people and critical infrastructure, mostly centered in the central and southern Sierra Nevada region of the state.
“The number of dead and dying trees has continued to rise, along with the risks to communities and firefighters if a wildfire breaks out in these areas,” said Randy Moore, regional forester of the USDA Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Region. “It is apparent from our survey flights this year that California’s trees have not yet recovered from the drought, and remain vulnerable to beetle attacks and increased wildfire threat. The USDA Forest Service will continue to focus on mitigating hazard trees and thinning overly dense forests so they are healthier and better able to survive stressors like this in the future.”
Moore continued, “To increase the pace and scale of this important work, we need to fix how fire suppression is funded. Last year fire management alone consumed 56 percent of the USDA Forest Service’s national budget. As fire suppression costs continue to grow as a percentage of the USDA Forest Service’s budget, funding is shrinking for non-fire programs that protect watersheds and restore forests, making them more resilient to wildfire and drought.”
USDA Forest Service
Though California received record-breaking rains in the winter of 2016-2017, the effects of five consecutive years of severe drought in California, a dramatic rise in bark beetle infestation and rising temperatures have led to historic levels of tree die-off. The Tree Mortality Task Force (TMTF), with support from the Governor’s office and comprised of more than 80 local, state and federal agencies and private utility companies, continues to remove hazardous dead trees. To date, the TMTF members have collectively felled or removed more than 860,000 dead trees; this includes more than 480,000 dead trees felled or removed by the USDA Forest Service.
The TMTF members are using a triage approach to this tree mortality crisis, first focusing on public safety by removing dead and dying trees in high hazard areas. To further improve forest health, the USDA Forest Service and CAL FIRE have increased their pace and scale of prescribed fire. The USDA Forest Service has treated more than 55,000 acres and CAL FIRE has completed more than 33,000 acres in fuel treatment projects. By combining tree removal with prescribed fire, crews will be able to decrease overly dense stands of trees, reduce greenhouse gases and protect communities across the state.
“Tree mortality at this magnitude takes on-going cooperation between public, non-profit and private entities,” said Chief Ken Pimlott, CAL FIRE director and California’s state forester. “California’s forests are a critical part of the State’s strategy to address climate change. By working together and using all the resources at our disposal we will be able to make more progress towards our common goal of healthier, more resilient forests that benefit all Californians.”
With record breaking levels of tree die-off, the TMTF has used this event as an opportunity to collaborate on several fronts: from public workshops about reforestation, public outreach in urban and rural areas, and awarding more than $21 million in grants aimed to protect watersheds, remove dead trees and restore our forests. The TMTF continues to collaborate on the efficient use of resources to protect public safety and build consensus around long-term management strategies for California’s forest lands.
“The Tree Mortality Task force has provided an essential venue for coordination of response efforts, exchange of ideas, reporting and accountability for the ongoing statewide response to this incident,” said Supervisor Nathan Magsig of Fresno County. “Leadership from the Governor’s Office, CAL FIRE and Office of Emergency Services has helped to ensure county issues are heard and addressed. Monthly coordination of the 10 most impacted counties has resulted in a more effective use of resources and has allowed counties to share ideas and successes.”
With a staggering 129 million dead trees in the state, the work of the task force is far from over. The strong foundation built will continue to be an advantage as the TMTF continues to address tree mortality and its impacts.

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe