
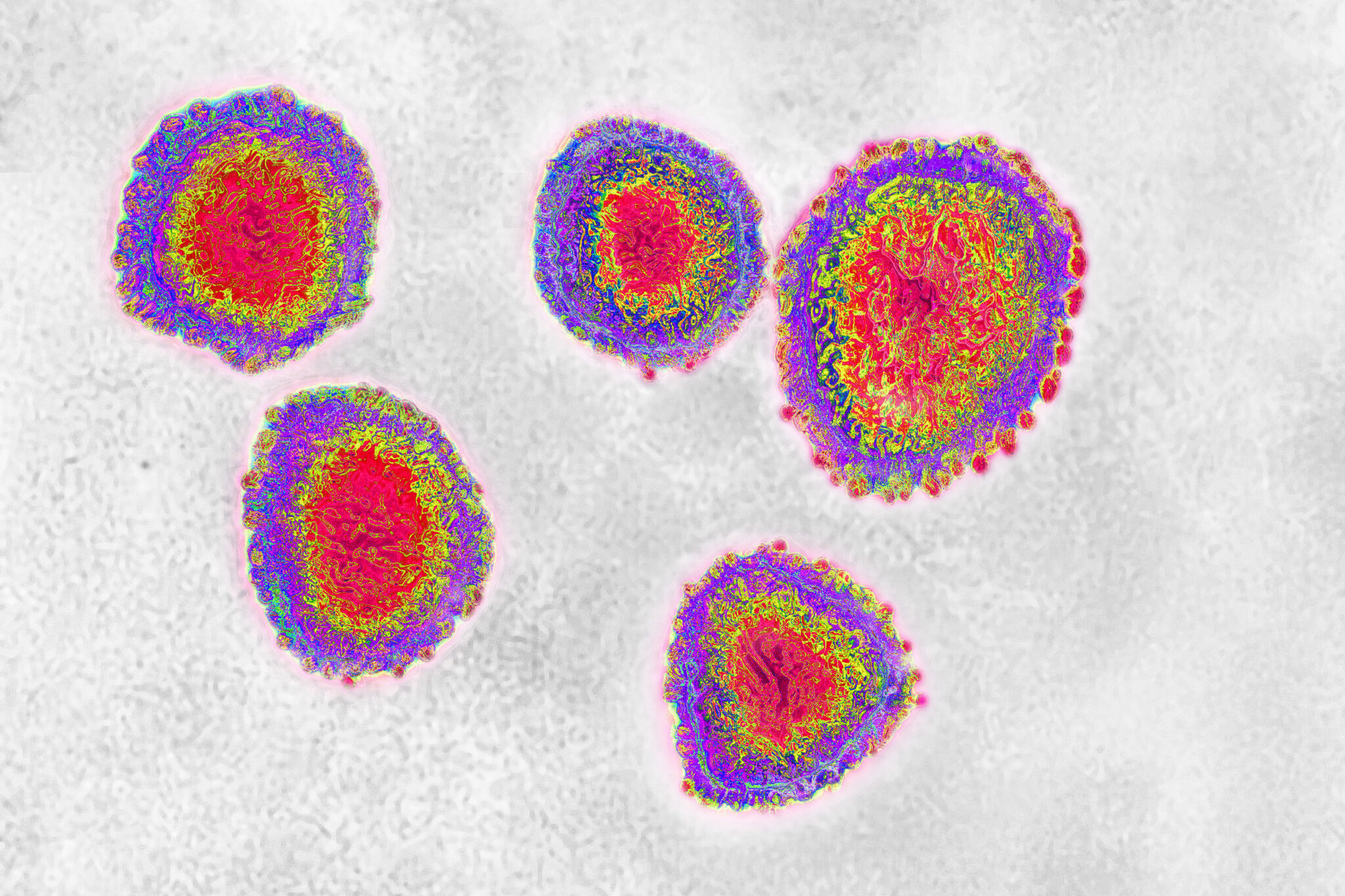
The human coronavirus causes respiratory infections (colds), and gastroenteritis. Cavallini James / BSIP / Universal Images Group / Getty Images
On Dec. 31, 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) country office in China was informed of 27 patients with pneumonia of unclear cause in Wuhan — a metropolis with 19 million inhabitants in Hubei province.
The municipal health commission reported that many of the infections could be attributed to visits to the fish market, which also sells live animals other than fish. The market hall was then closed until further notice and has been disinfected.
By Jan. 5, 59 patients had been identified. Seven of them are in a critical condition, according to a report by the Robert Koch Institute; no deaths were reported.
In addition, South Korea reported that its first suspected case involved a 36-year-old Chinese woman who visited Wuhan last month, according to authorities. She is being treated in a hospital in Bundang, south of Seoul.
The Good News
Eight patients are currently considered cured and have reportedly left the hospital.
Having identified the virus, experts are one step further in their search for what is triggering the mysterious lung disease.
The pathogen’s gene sequence has been deciphered, according to the head of the team of Chinese experts, Xu Jianguo.
He said the cause is a new type of coronavirus found in the blood and saliva of 15 patients. An investigation into what brought about the outbreak will continue.
Gauden Galea, a WHO representative in China, also confirmed the discovery of the new strain of the coronavirus in a statement.
According to the WHO, the quick preliminary identification of the novel virus is a notable achievement and demonstrates China’s increased capacity to manage new outbreaks.
Chinese authorities have made a preliminary determination of the cause of #pneumonia in Wuhan as a novel (new) #coronavirus. @WHO continues to monitor the situation closely and is ready to support #China to investigate and respond to this outbreak. https://t.co/0zR6iZWrcm (1/7)
— World Health Organization (WHO) Western Pacific (@WHOWPRO) January 9, 2020
What are coronaviruses?
Coronaviruses were first found in humans in the 1960s. The name is derived from their appearance under the microscope: The peplomers, the outwardly protruding protein structures of the virus envelope, are arranged in the form of a crown (from Latin: corona).
Coronaviruses are common and infections are often harmless with patients developing only flu-like symptoms, such as fever, cough and shortness of breath. Gastrointestinal complaints, especially diarrhea, can also occur. The incubation time for a coronavirus can vary from a few days to two weeks.
However, coronaviruses are also dangerous and can mutate. They are RNA viruses and have high genetic variability, meaning they can easily overcome barriers between different species. Often, an outbreak among humans originates with other mammals, rodents or birds.
As a consequence, the infections also can take more severe paths, causing respiratory distress and pneumonia, which can even lead to death.
In 2002 and 2003, for example, the aggressive coronavirus SARS-CoV triggered an epidemic. At that time, more than 8,000 people in 29 countries became ill and 774 people died of SARS-CoV. In 2012, the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) was discovered and spread across the Arabian Peninsula.
In both cases, experts suspect animals were the source. The first infections were typical zoonoses — cases where pathogens manage to jump from an animal host to a human host.
How is the virus transmitted?
Zoonoses can be transmitted through direct contact between animals and humans as well as — like with many germs — simply through the air, such as by coughing or sneezing.
But there are many other ways of infection, for example through food or vectors. A mosquito, tick or other insect can transport a pathogen from the host to another organism without becoming ill itself.
In addition, zoonoses can also be transmitted via food, for example when eating meat or animal products. If these are not sufficiently heated or if they were prepared under unhygienic conditions, they also represent a source of infection.
Lunar New Year: Be safe
Compared to the major instances of SARS and MERS, the current coronavirus outbreak is small, but experts said it should not be underestimated.
China is, therefore, exercising caution regarding the Chinese Lunar New Year celebrations in late January. Millions of people travel in buses, trains and airplanes to celebrate the holiday.
Wang Yang, the Chinese Transport Ministry’s chief engineer, said authorities will step up efforts to prevent the pneumonia outbreak from spreading further during the holiday period, including ensuring proper disinfection in major public transportation hubs like airport and train stations.
Other Asian countries also stepped up precautions on entry, especially for travelers from Wuhan, and introduced fever controls to prevent the feared spread of the virus. To date, there are 16 suspected cases in Hong Kong, and a possible patient has been reported in Singapore. Not in all of the cases have a direct connection to Wuhan.
How to protect yourself?
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released a statement warning travelers to Wuhan to avoid animal markets and contact with animals or uncooked meat. People in the area should also avoid the sick and wash their hands frequently with soap and water.
Those who have been to Wuhan and feel ill should seek medical help immediately and avoid contact with others, the report said.
Before the doctor is consulted, the practice or clinic should be informed about the travel history and symptoms.
The WHO did not issue a specific travel warning.
Reposted with permission from Deutsche Welle.
- Black Death Is Back! Two Cases of Plague Confirmed in China ...
- Unknown Lung Disease in China - EcoWatch

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 