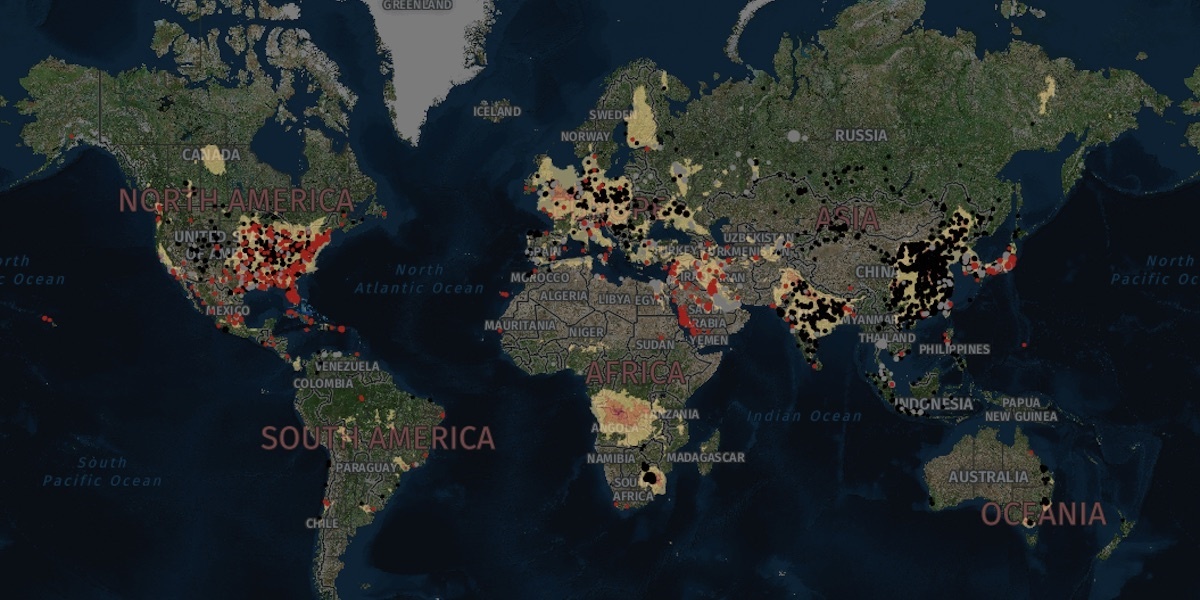
Nitrogen dioxide pollution around the world. Greenpeace
Greenpeace has revealed the world’s largest nitrogen dioxide (NO2) air pollution hotspots across six continents, and identified Mpumalanga, South Africa as the biggest NO2 hotspot, even outranking areas in China, India and the U.S.
The lush, green province is home to the southern half of Kruger National Park and the iconic Blyde River Canyon. At the same time, it’s home to a dozen coal fired power plants owned and operated by the power utility Eskom.
NO2 is a dangerous pollutant that’s emitted when fossil fuels such as coal, oil, gas or diesel are burned at high temperatures, and also comes from transportation, forest fires and crop burning. The gas can react to create smog, acid rain and is central to the formation of fine particles and ground ozone, which are both linked to adverse health effects.
“The health toll from these emissions shows the need for an energy revolution that eliminates our reliance on fossil fuels: renewable power generation, energy efficiency, transport and mobility systems that rely less on private cars, as well as electric vehicles,” Greenpeace explained in a report.
Burning coal releases NO2 into the air. NO2 is a dangerous air pollutant that causes asthma and lung cancer. Residents in communities near coal-fired power stations in Mpumalanga are concerned. This air pollution is having a severe impact on their health. #NO2Coal #EndCoal pic.twitter.com/oiuoaa8hXu
— Greenpeace Africa (@Greenpeaceafric) October 29, 2018
Greenpeace’s new analysis is based on data produced by the European Space Agency’s Sentinel 5P satellite, which measures air pollution in the atmosphere, between June to August 2018.
Besides Mpumalanga being the biggest NO2 hotspot, the findings show that China has the world’s highest number of individual hotspots, followed by the Middle East, the European Union, India, the U.S. and the Democratic Republic of Congo, Quartz Africa noted from the study.
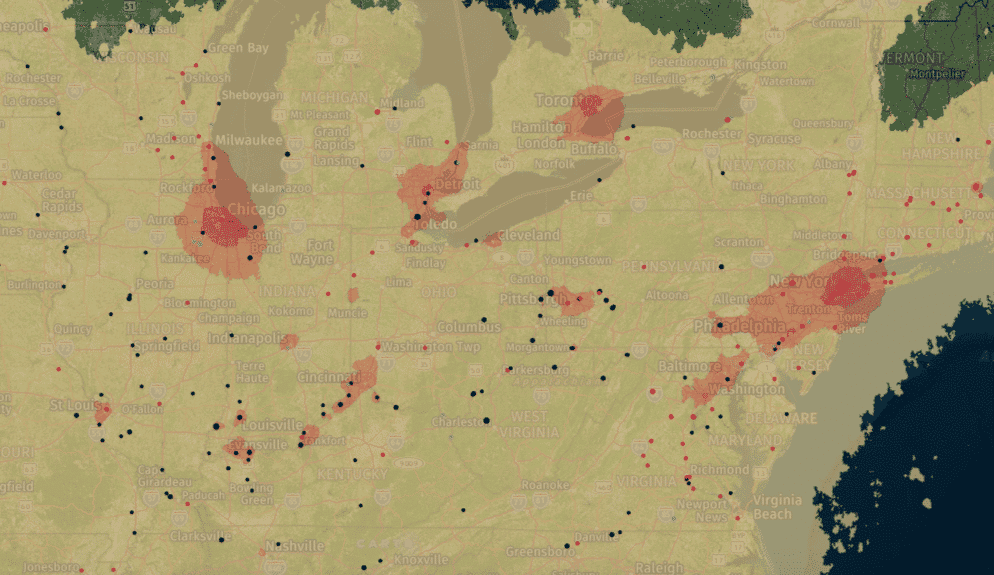
NO2 pollution in the United States. The colored dots represent a power plant. The colored clouds show the level of NO2 in the area. The darker—or pinker–the cloud, the higher the concentration. Greenpeace
An interactive mapping of global NO2 pollution can be seen here.
“The map also points to the impact of emissions regulations in some places. While there are plenty of coal plants in the U.S., NO2 concentrations near plants in India, South Africa, Australia and Indonesia stand out much more. In these countries, there has been a failure to enforce meaningful pollution standards, or to implement them,” Greenpeace’s journalism unit, Unearthed, pointed out.
5 Ways Trump Is 'Gaslighting' Us on U.S. Air Pollution Levels #TrumpWatch #TrumpTweets #CleanAir #TuesdayThoughts #WeWillNeverBeTheSame @lakotalaw @youthvgov
Heard about the latest false tweet? No. We are NOT the nation with the cleanest air. https://t.co/Gg5DEBRDTc
— EcoWatch (@EcoWatch) October 23, 2018
Greenpeace researchers noted that the extreme NO2 pollution levels emanating from Mpumalanga blow into the nearby cities of Johannesburg and Pretoria.
“Because South Africa’s coal-belts are hidden from view for the majority of South Africans, it can be easy to pretend that they don’t actually exist. The reality is that coal extraction and burning has devastating impacts on the people living in the area,” Melita Steele, the senior climate and energy campaign manager of Greenpeace Africa, said in a press release. “This satellite data now confirms that there is nowhere to hide: Eskom’s coal addiction in Mpumalanga means that millions of people living in Johannesburg and Pretoria are also impacted by the pollution from coal.”
THREAD: @KhuluPhasiwe your tweets seem to be in response to news that Mpumalanga has the world's dirtiest air: https://t.co/TH5a3upQXt. @Greenpeaceafric believes that Eskom cannot 'offset' its pollution from ancient coal power & is refusing to comply with air quality legislation https://t.co/sUmYQPfv05
— Melita Steele (@Melita_Steele) October 29, 2018
Cities such as Santiago de Chile, London, Paris, Dubai and Tehran were also singled out by the analysis due to transport-related emissions.
“Air pollution is a global health crisis, with up to 95 percent of the world’s population breathing unsafe air,” Steele continued in the press release. “South Africa is a significant global hotspot with its high concentration of coal power stations and its weak air pollution standards. Our Government urgently needs to come up with an action plan that protects millions of people, instead of dirty coal power stations.”
Steele explained the new findings in the video:
Mpumalanga is the world’s biggest air pollution hotspot
www.youtube.com

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe