Here Are Three Sustainable Seafood Brands to Know for World Oceans Day

 Why you can trust us
Why you can trust us
Founded in 2005 as an Ohio-based environmental newspaper, EcoWatch is a digital platform dedicated to publishing quality, science-based content on environmental issues, causes, and solutions.
If you love seafood but the documentary “Seaspiracy” and seafood fraud have you worried, there may be a solution: seafood that is actually sustainable. These foods come from the sea but are caught and processed in ways that either don’t harm or help regenerate fragile ecosystems. Some even help in the fight against the climate crisis.
Just in time for World Oceans Day on June 8, three companies are using transparency, technology and traceability to innovate the seafood space. Whether you’re enjoying a kelp burger, a piece of ahi tuna jerky or a fresh lobster tail that you can follow from the fisher to the table, these entrepreneurs are producing seafood to ensure that oceans remain healthy and productive.
1. KnowSeafood: Using blockchain to trace quality seafood
KnowSeafood is an online seafood market touting high-quality, sustainable and natural seafood. The idea is that “your seafood has a story,” the company motto notes, and KnowSeafood wants you to know it even before you purchase anything.
Consumers can track the entire history of a seafood product, including a timeline and map, on KnowSeafood’s website or on cellphones. It’s possible to learn when and where the product was caught, by who, what methods were used, when it was frozen and when it will be delivered. Harvesters are required to upload catch information, which becomes the first block of information in the blockchain. According to Investopedia, blockchains are irreversible datasets that are readily available to view and “establish an exact and transparent order of events.” At each processing step, the complete and chronological block of information about how the product has been handled is attached to the chain that follows the fish.
The 100 percent traceability and transparency “brings trust to the seafood chain,” KnowSeafood Co-Founder Dan McQuade told EcoWatch. By only partnering with trusted, sustainable harvesters and tracing products from them directly to consumers, KnowSeafood has “virtually eliminated much of the fraud and abuse that plagues the seafood industry,” a company representative said.
“I’ve worked in the seafood industry for decades and know exactly what happens when seafood goes through too many middlemen,” McQuade said. “That’s where additives, antibodies, rampant seafood fraud, unsustainable fishing and safety problems happen.”
Blockchain traceability technology and transparency are available for everything KnowSeafood offers, including New England lobsters that are sorted to avoid reproductive and egg-bearing lobsters; hand-harvested Peruvian bay scallops; and aurora salmon farmed and fed an entirely plant-based diet of corn husk and kelp, McQuade shared. The company’s newest venture is the world’s first farmed, entirely plant-based fed, non-GMO shrimp from Ecuador.
More information is available at KnowSeafood.com.
2. Akua: Using regenerative ocean farming to create kelp burgers and jerky
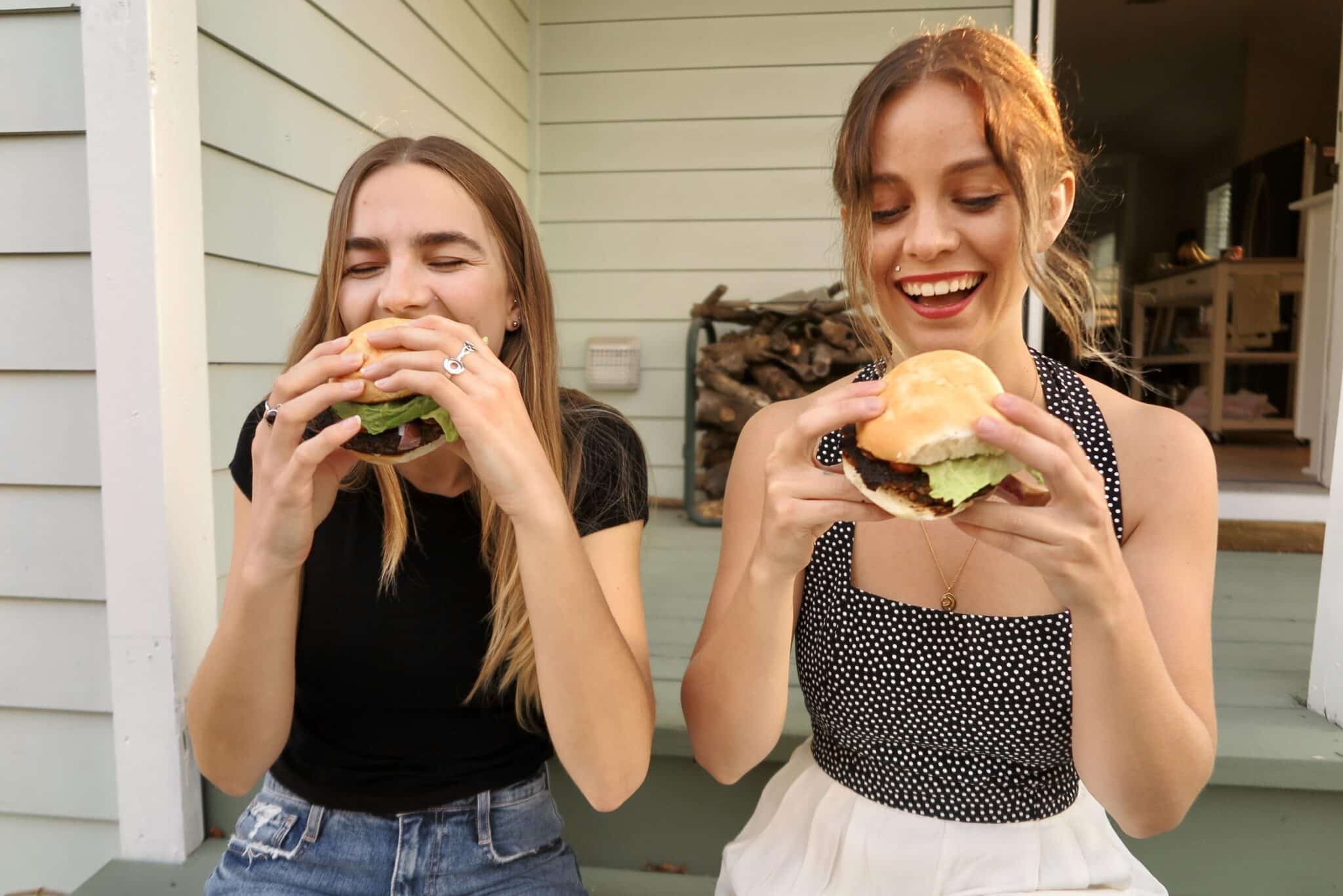

Akua has introduced sustainable kelp burgers. Akua
“Sustainable seafood is sourcing food from the sea that leaves the oceans more or less as they were found, resulting in zero impact. Given the state of our oceans, sustainability isn’t enough right now,” Akua Co-Founder and CEO Courtney Boyd Myers told EcoWatch.
That’s why her company focuses on ocean farming kelp. Boyd Myers explained how kelp grows “via photosynthesis, without the need for freshwater, land, fertilizer or feed.” The algae farming process sequesters carbon and nitrogen from the water, much like plants on land do. According to Akua, this helps to reduce local ocean acidification, which also helps lower rising ocean temperatures, increase biodiversity and support other marine life.
This process is “much more than sustainable — it’s a regenerative practice” that leaves the oceans and planet healthier, Boyd Myers said.
In the first six months before official launch, Akua sold 22,000 kelp burgers and another 10,000 during its May 20 launch week. According to New York Times Food, the burgers are best served off a hot griddle.
“2021 is definitely the summer of the kelp burger,” Boyd Myers added. “We’re seeing a big shift in all forms of agriculture from sustainable to regenerative because it’s hugely important that we leave the planet better than it is right now for future generations. We can’t just stop, we have to reverse. We need to grow food in a way that is healing and not just sustaining.”
More information is available at Akua.co.
3. Pescavore: Using local, minimally harmful fishing methods to create ahi tuna jerky

Wild-caught tuna promotes responsible tuna fisheries management. Healthy Oceans Seafood Company
According to Healthy Oceans Seafood Company CEO and Co-Founder Matthew Owens, the company that owns Pescavore, the brand focuses on innovative fishing technology, local and traceable fisheries and sustainable packaging.
For example, the brand’s ahi tuna jerky is a single-serve, wild-caught product that promotes responsible tuna fisheries management.
Owens was frustrated that more than 90 percent of seafood consumed in the U.S. is imported, despite having the world’s second-largest exclusive economic zone (which grants jurisdiction over natural resources) and access to locally harvested and sustainable seafood.
“In addition to a large carbon footprint, an over-reliance on imports creates traceability challenges and thus increases the risk of illegal, unreported and unregulated fish entering the market,” Owens told EcoWatch. That’s why all of Pescavore’s tuna is landed in Los Angeles and made in the U.S. The focus on local catches also returns economic value to domestic coastal communities, which is critical in the post-pandemic economy, Owens added.
Pescavore only sources from healthy and abundant fish populations, such as free school yellowfin tuna caught in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, and avoids overfished and sensitive species.
“We source tuna that is unassociated with dolphins or fish aggregating devices, and caught without longlines,” Owens shared. The selective fishing methods also create “less carbon footprint than pole and line fishing and with almost zero bycatch” of dolphins, sea turtles and other sensitive species, he added.
Pescavore snacks are shelf-stable for up to 18 months, while innovative pouch packaging saves 96 percent of space compared to caned tuna storage. This further reduces the product’s carbon footprint.
“One truckload of our packaging has the capacity of 28 truckloads of tin cans,” Owens said. “The pouches are made in part from recycled material and are recyclable after use in Europe and hopefully, with improved systems, will also soon be recyclable in the USA.”
More information is available at https://pescavoreseafood.com.
Subscribe to get exclusive updates in our daily newsletter!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy & to receive electronic communications from EcoWatch Media Group, which may include marketing promotions, advertisements and sponsored content.

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 



