
Rail Travel Is Cleaner Than Driving or Flying, but Will Americans Buy In?

The Northeast Corridor sees millions of riders a year, but expanding rail in the U.S. is always fraught. Loco Steve, CC BY-SA
By Andreas Hoffrichter
Transportation represents a large portion — about 29 percent — of U.S. emissions, and the share has been rising in recent years. Rail proponents often argue that investment in trains and public transportation is a key part of making transportation cleaner, and indeed, the Green New Deal calls for greatly expanding high-speed rail.
I’m a scholar of rail, and it’s clear to me that the quickest way to decrease greenhouse gases from transportation is to travel by train and move goods by rail instead of on the road or by air.
To explain why, it’s worth comparing rail to other modes of transportation on energy consumption and emissions, and to look at some of the developments that can make rail more widely used in the U.S. and less reliant on fossil fuels.
Energy and Emissions Profiles
Transportation by rail is a major part of the transportation system in most countries, including in the U.S., which has the longest freight railway system in the world with approximately 140,000 miles. Rail passenger services are essential in many areas, primarily in population centers such as New York and Chicago, and intercity rail has a significant market share in some corridors, such as the Northeast. Rail also offers long-distance routes connecting many smaller communities with each other and the large metropolitan areas in the country.
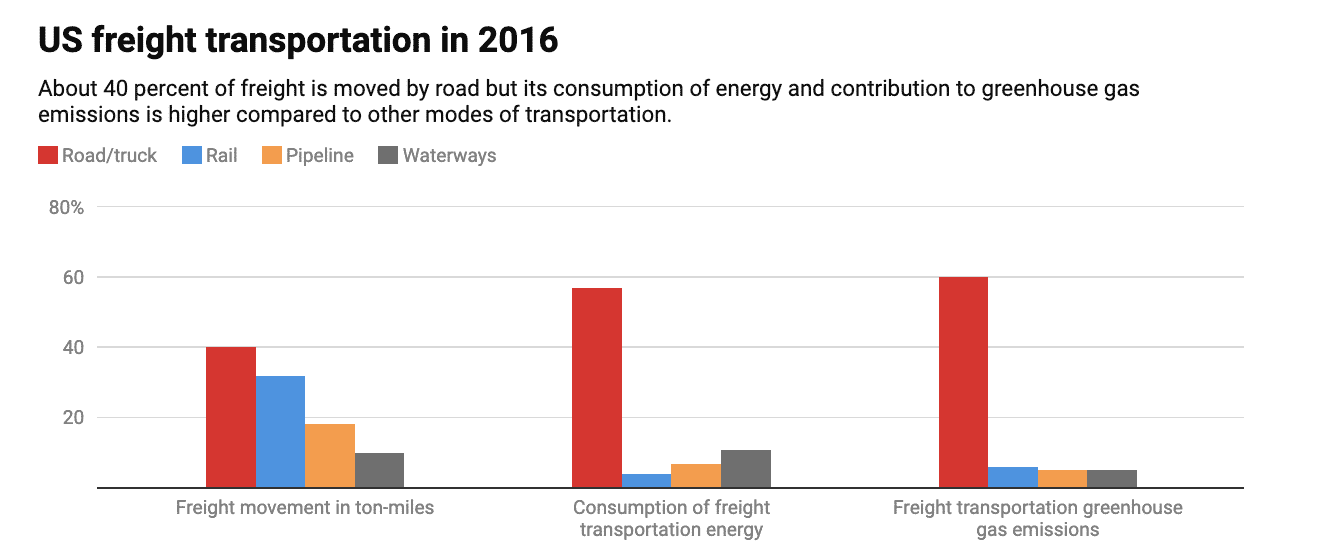
Chart: The Conversation, CC-BY-ND
Data show that rail has a significantly lower energy footprint than trucks and passenger cars. Rail transport, with hard steel wheels on steel rail, has lower resistance to motion than road transportation. And the convoy formation of individual rail cars into trains also adds to its better energy and environmental performance.
A common measure for transportation capacity is ton-miles for freight and passenger-miles for passengers to indicate that a ton of freight is moved for one mile and for passenger systems that a passenger is moved for one mile.
Freight rail accounts for about one-third of the ton-miles and consumes only about 2 percent of the transportation energy in the U.S. The higher efficiency can be illustrated this way: On average, freight railroads move a ton of cargo for around 479 miles on a gallon of fuel, which is about 11 times more energy-efficient than trucks on a ton-mile basis.
Passenger rail is around three times more efficient than a car on a passenger-mile basis at current occupancy levels. The lower energy consumption leads to lower greenhouse emissions.
Data show that rail has a significantly lower energy footprint than trucks and passenger cars. Rail transport, with hard steel wheels on steel rail, has lower resistance to motion than road transportation. And the convoy formation of individual rail cars into trains also adds to its better energy and environmental performance.
A common measure for transportation capacity is ton-miles for freight and passenger-miles for passengers to indicate that a ton of freight is moved for one mile and for passenger systems that a passenger is moved for one mile.
Freight rail accounts for about one-third of the ton-miles and consumes only about 2 percent of the transportation energy in the U.S. The higher efficiency can be illustrated this way: On average, freight railroads move a ton of cargo for around 479 miles on a gallon of fuel, which is about 11 times more energy-efficient than trucks on a ton-mile basis.
Passenger rail is around three times more efficient than a car on a passenger-mile basis at current occupancy levels. The lower energy consumption leads to lower greenhouse emissions.
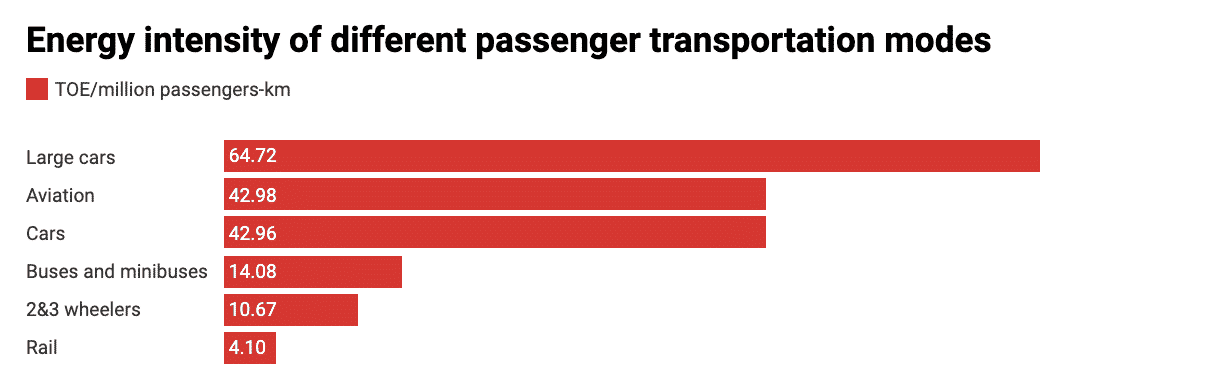
TOE is tonne of oil equivalent, a unit of measure to indicate the amount of energy released in burning one metric ton of crude oil.
Chart: The Conversation, CC-BY-ND. Source: International Energy Agency. Get the data.
How U.S. and European Rail Differ
Often there is the perception that the U.S. lags behind other countries when it comes to rail, but in many cases that is not true. The country has, arguably, the best freight rail system in the world, which is owned, operated and financed by private companies. Passenger service in specific corridors is comparable with the European counterparts: for example, in the Northeast. On long-distance routes and in less densely populated areas, however, there are often empty seats on Amtrak trains.

The U.S. freight train system is more developed than passenger rail, which is the opposite of Europe.
The primary difference between Europe and North America could be summarized like this: In America there is a freight rail system with some passenger, while in Europe there is a passenger rail system with some freight — the emphasis is different.
A further difference is that the rail network is private in the U.S. and operated to yield a profit, while in most other countries the rail infrastructure is owned by the government (similar to the freeway system in the U.S.) and heavily subsidized.
To Compete With Air for Passenger Transportation
Running passenger and freight trains on the same lines is possible but poses many challenges, as the characteristics of the two train types are very different; freight trains tend to be long, heavy and comparatively slow, while passenger trains are short, fast and comparatively light. If there are not too many trains on a line, this mixed traffic can be managed, but if there are a lot of trains, then separate infrastructure is the way forward.
When journey times are less than four hours, people usually prefer to travel by train instead of alternative options, such as air or road. For many corridors in the U.S. it would be necessary to upgrade existing lines or to build new infrastructure to achieve competitive journey times.
For the high-speed rail projects in California, which the state recently decided to scale back, and Texas, where trains would be able to travel at speeds of 200 miles per hour or more, those states are building new infrastructure. Higher-speed options often allow existing rail tracks to be upgraded to accommodate speeds of around 110 miles per hour to around 125 miles per hour, and such projects are being implemented in Florida and the Midwest.
Routes to Better Environmental Performance
The majority of trains in the U.S. are diesel-electric, where a diesel engine runs a generator, supplying electric traction motors that turn the wheels. However, electricity can also be supplied by the grid to trains via wayside infrastructure, and this option accounts for about 4.5 percent of rail energy, more than for any other mode, with the majority being used in transit and commuter operation, and some intercity rail. Therefore, when the electricity generation mix becomes less greenhouse gas-intensive, those rail systems automatically follow.
For the lines where wayside electrification is not economically feasible — imagine routes that are long, such as Chicago to Los Angeles — or where traffic is relatively low, rail will continue to rely on on-board electric power generation.
Rail is developing options to reduce emissions for lines without wayside electrification too, with advanced diesel engine technologies, and exploration of less polluting energy options, including natural gas. Florida East Coast Railway has converted the majority of their locomotives to liquefied natural gas.
Having batteries to supply power to trains can significantly reduce or fully avoid conventional wayside electrification, decreasing cost and visual impact as no overhead wires are necessary on the right-of-way. These are suitable for relatively short distances and where power demand is low, such as light rail and streetcars. Detroit’s QLine, for example, operates 60 percent on battery power, or “off-wire.”
Hydrogen fuel cell applications to rail, often referred to as hydrail, enable long range with a lower environmental footprint than diesel, and such trains for regional passenger service are already in operation in Germany. In the U.S., the technology is being investigated by some passenger and transit railways, including in North Carolina, and its use for freight rail is being explored as well.
Even without these advances, rail is already more environmentally friendly than road or air. Dramatically expanding rail use, particularly passenger service, will require government investment in more frequent service on existing lines, starting service to areas that don’t have access to rail currently, reducing journey times and building out a larger passenger rail network.
Will High-Speed Rail Ever Get on Track in the U.S.? https://t.co/lpV1hWxPeO #Transportation #Climatechange #China pic.twitter.com/IgxSstBIJv
— Tom DeRosa (@RenewableSearch) March 25, 2019
Andreas Hoffrichter is the executive director of the Center for Railway Research and Education, Michigan State University.
Disclosure statement: Andreas Hoffrichter is employed by Michigan State University in the Center for Railway Research and Education and is researching low and zero-emission railway motive power technologies. The Center receives grants from state governments to investigate alternative motive power technologies.
Reposted with permission from our media associate The Conversation.
- Germany Considers Free Public Transport to Fight Air Pollution ...
- 'Aggressive' Railway Expansion Could Cut Emissions
- World’s First Battery-Powered Freight Train Unveiled in Pittsburgh

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 