
Solar Panel Glass (Don't Overlook This When Going Solar) (2024)
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- Why glass is used in panel manufacturing
- What type of glass is used for photovoltaic panels and which is best
- Why panels with cheap glass should be avoided
Each product and or company featured here has been independently selected by the writer. You can learn more about our review methodology here. If you make a purchase using the links included, we may earn commission.
Why Is Glass Used in Solar Panels?
Virtually every rooftop solar panel you see has a protective sheet of glass over the solar cells. Glass is one of the key components of a photovoltaic (PV) panel, and the material is used for very specific reasons.
When manufacturing solar panels glass is seen as a key component for its durability, transparency, stable nature, variability and ability to further an eco-friendly agenda of recycling. Due to the nature of all of these added benefits, it is no wonder that many high rated solar panel manufacturers choose glass. Of course there are also some cons- weight, and fragility are just two of them but fiberglass has often come in to play and now the solar industry has even developed thinner solar panels and flexible solar panels made of glass. Not to mention glass is often an integral part of how solar panels work as glass helps increase the efficiency of panels due to its reflective nature.

Blue Raven Solar
Pros
- Industry-leading in-house financing
- Competitive pricing
- Excellent reputation
Cons
- Doesn't offer solar batteries (coming 2022)

Blue Raven Solar
Pros
- Industry-leading in-house financing
- Competitive pricing
- Excellent reputation
Cons
- Doesn't offer solar batteries (coming 2022)
Durability
While glass is not quite as transparent as plexiglass and some other man-made materials, it possesses other qualities that make it ideal for panel manufacturing.1 One of the primary qualities is durability.
The PV cells encapsulated in your solar modules are fragile and need to be kept safe from any moisture. Electricity and water don’t mix, so it’s important to have a highly protective and durable covering over the internal components of a PV panel.
Glass — and especially tempered glass — is a highly durable building material that couples transparency with longevity and adequate protection. It’s impermeable to water and can stand up to a lot of abuse, including strikes from hail, blown debris and even fallen tree limbs in some cases.
Transparency
The solar modules you install on your home will, of course, depend on sunlight to produce electricity. The more sunlight that reaches the solar cells, the more power your solar energy system will generate.
Glass is highly transparent and lets up to 99.95% of all light pass through it.2 This means the large majority of the sunlight hitting the face of your panels will be transmitted to your solar cells for energy production. Glass varies in degrees of transparency, but most types of clear glass are suitable for PV panels.
Transparent solar panel glass is especially important when installing bifacial panels or Building Integrated Photovoltaics materials (BIPV). Light getting through bifacial panels can be absorbed by the underside of the cells, and BIPV glass allows sunlight into your living space while still capturing some for clean energy production.
Stability

Since your panels will be outside and exposed to the elements at all times, the covering on your panels needs to be durable — but also stable in a variety of conditions. It needs to resist expansion and contraction in those conditions to ensure that your PV cells remain safe and dry.
Glass has a high degree of stability in virtually all conditions your panels may endure. These include:
- Extreme heat in the summer
- Extreme cold in the winter
- Prolonged exposure to moisture
- Prolonged exposure to dry conditions
Additionally, your panel covering needs to be stable under solar irradiance. Some building materials will expand and contract with exposure to sunlight, and others will fade and can become cloudy, which would reduce light transmission. Glass resists changes with prolonged exposure to the sun.
Variability
Another benefit of using glass to cover PV panels is the number of options the manufacturer has for improving panel performance and durability. These include:
- Anti-reflective coatings to improve light transmission
- Tempering to increase strength and durability
- Making the glass electrically conductive to improve panel efficiency and protection3
- Reflective inner surface to trap sunlight inside the panel
Recyclability
Finally, glass is a recyclable material. A major draw of installing a solar panel system is reducing your emissions in the fight against climate change. Panels made out of recyclable materials help achieve that goal.
What Types of Glass Do Solar Panels Use?
Solar manufacturers have a few options for the type of glass they use in their panels. We’ll discuss the most popular options below.
Plate Glass
Plate glass is the easiest type to manufacture, but it’s about ¼ as durable and impact-resistant as tempered glass. When it’s damaged, it breaks into large pieces that are dangerously sharp on the edges. Plate glass is typically found in thin-film panels.
Tempered Glass
Tempered glass is a more expensive option but is far better suited for solar manufacturing. This glass is highly resistant to impact and damage. When it breaks, it shatters into tiny pieces that lack sharp, hazardous edges. Tempered glass is most often found in monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels.
Soda-Lime Glass
Soda-lime glass is made from silicon dioxide, sodium oxide and calcium oxide. It’s the most common type of glass used for windows and PV panels. It can be manufactured with a low iron content to improve light transmission.
Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass is more costly to manufacture, but it has an even higher transmission capacity than soda-lime glass to improve solar efficiency. It can also stand up better to extreme heat without expansion.
Lead Crystal Glass
Lead crystal glass has a high clarity rating, which means the highest level of light transmission. It’s also the most resistant to expansion in extreme heat. However, it’s more costly to produce than the other options.4
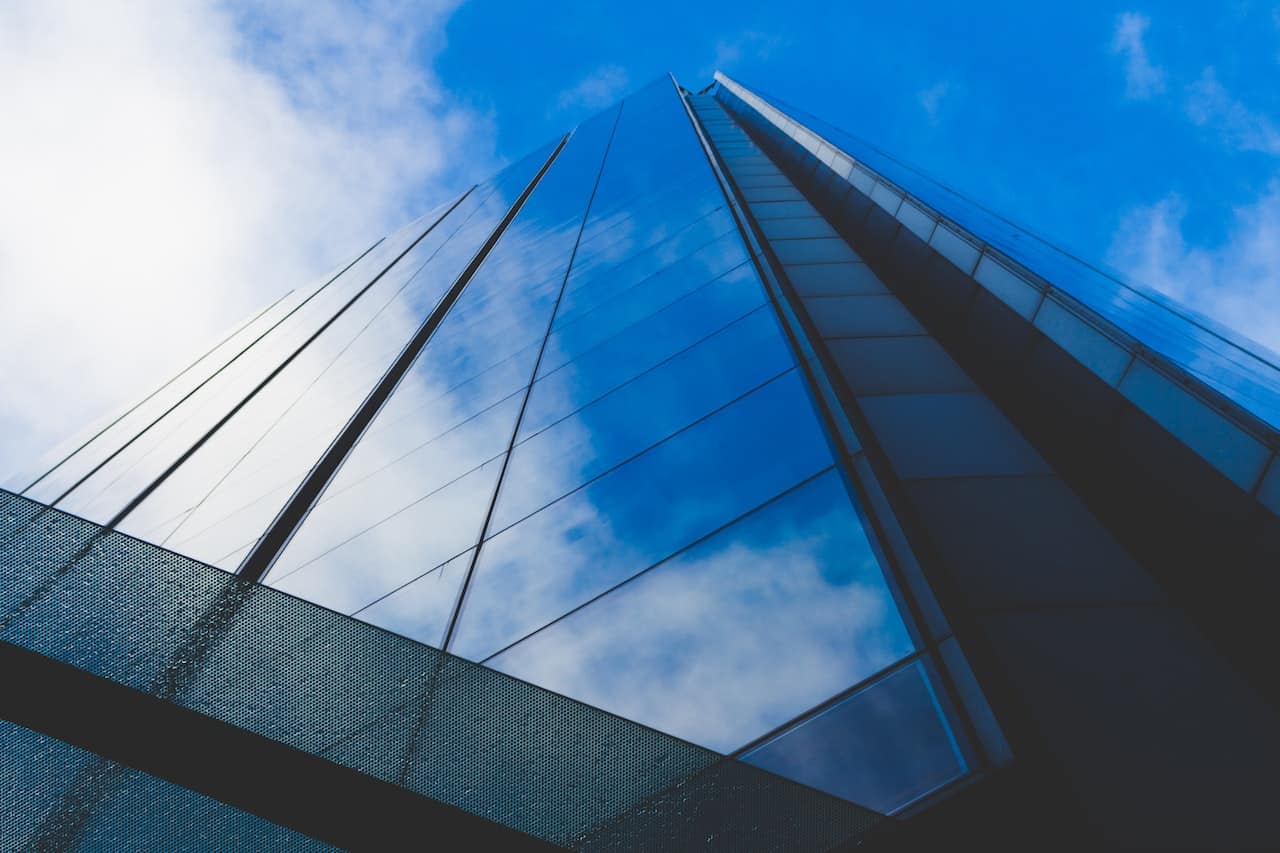

A Word on Fully Transparent Solar Glass Panels
Researchers at Michigan State University (MSU) developed the first fully-transparent solar panel. The solar concentrator provided clear glass panels for use as windows, but the specialized glass product also harnessed some of the solar energy passing through for electricity production.
This glass product makes it possible for visibly clear glass windows to absorb some of the non-visible wavelengths of sunlight — infrared light and ultraviolet light. The result is a transparent glass surface that can improve energy efficiency of homes and make solar viable for use in larger office buildings, including skyscrapers.
This glass sheet product could be revolutionary for renewable energy. It allows solar windows to become a viable option for sustainability for high-square-foot buildings that wouldn’t benefit from a traditional rooftop system.
What Are the Main Properties of Solar Panel Glass?
Glass is the primary component — by weight — of solar panels, so a good deal of the panel efficiency and performance hinges on the glass used. In the sections below, we’ll discuss the main properties of solar panel glass that affect your panel performance and longevity.
Durability
Since PV panels will be outside and exposed to the elements, it’s important that the glass used in manufacturing can stand up to some abuse. Intense thunderstorms, tornadoes, hurricanes, tropical storms and hail storms can all put your rooftop panels at risk of damage, so a higher degree of durability is an essential factor when producing PV panels.
As mentioned above, tempered glass is the superior option over plate glass for solar modules. Tempered glass is about four times as strong as plate glass, and that strength comes without any loss of light transmission.5
Solar Radiance
It’s important for photovoltaic glass to be durable, but it also needs to transmit light to the PV cells. Without a high degree of transparency and solar radiance — a measurement of how much solar energy can pass through the glass — durability doesn’t matter all that much, as energy production will fall steeply.
High-quality, clear solar panel glass can transmit nearly 100% of the light that hits it, which is ideal for PV panels. PV glass can also be coated on the outside with anti-reflective coatings to improve solar radiance.
Longevity

Solar systems are quite expensive, averaging around $29,970 before any tax incentives or rebates are considered. For these systems to be worthwhile for residential use, the equipment needs to persist for at least an average of 11 years, which is how long most panels take to pay for themselves in energy savings.
However, many homeowners need to see even longer equipment lifespans to be convinced that solar is a worthwhile investment. Therefore, it’s crucial that PV glass be able to stand up to the elements and resist:
- Fading, which decreases transmission and power production
- Clouding, which also causes solar production to plummet
- Expanding and contracting in heat, cold, moist and arid conditions, which can expose PV cells to dangerous conditions and lead to an increased risk of fire
Weight
The weight of the glass is another important consideration, as most solar arrays are roof-mounted and will need to be supported by the structure of your home. It’s possible to use thicker plate glass to improve strength and keep production costs down, but there is a limit to how much weight your roof can safely support.
Solar glass manufacturing needs to take into consideration not only the durability and transmission qualities of the glass but also how much it weighs. For this reason, it’s often a better option to use thin tempered glass for strength and solar radiance to ensure that a multi-kilowatt system can safely be installed on top of a home.
Anti-Reflective or Reflective Coatings
Finally, you should consider the coatings that are used in the solar manufacturing process.
Adding an anti-reflective coating to the outside face of the panel glass will reduce the amount of sunlight reflected off of the panel. This coating helps maximize the amount of solar energy reaching your PV cells for energy production. The result is a higher power generation capability.
Similarly, adding a reflective coating to the inside face of the panel glass will help with sunlight trapping. This coating will help keep solar energy that reflects off of your PV cells within the panel for energy production.
Risks of Using Cheap Glass in Solar Panels
At first glance, choosing a more affordable type of glass for your PV panels might seem like a great option. With the average solar PV system cost nearing $30,000 before incentives, most homeowners look for ways to keep costs to a minimum.
Unfortunately, opting for cheaper glass is almost never a good idea, as it can put your system production, your home and more in danger. We’ll discuss the primary drawbacks of cheap PV glass below.
Reduced Production Capacity
Perhaps most importantly, low-quality glass is at risk of clouding, discoloring and even warping in extreme heat. All of these changes can mean lower levels of sunlight transmission through your panel glass over time, which directly correlates to less energy production.
Solar systems save you money over time by providing energy savings. However, if solar production drops, so too will your potential savings. With low-quality glass, you’re at risk of significantly reduced savings over time, which could mean your savings never overcome your installation costs.
Lower System Value
Solar systems are expected to raise your property value by around 4.1% when you go to sell.6 Part of the reason for this is that a buyer will see the potential for energy savings and can deduct them from living expenses to see savings over time. However, this largely hinges on the lifespan of your system, and the warranty coverage included.
Panels with high-quality glass typically have longer and more robust warranty coverage because it’s at lower risk of damage and system failure. Buyers who purchase your home and still have years of coverage will see more value in your system overall.
Reduced Longevity
As mentioned above, cheap photovoltaic glass is less resistant to extreme heat, extreme cold and changes in moisture. Low-quality glass is more likely to expand and contract with changes in outdoor conditions, which means the panels are more likely to fail in a shorter amount of time.
Additionally, low-quality glass is more prone to damage from extreme weather, so there’s a chance your system won’t perform as intended for as long. This is especially true in areas at high risk of extreme weather, like those along the coast and states located in Tornado Alley.
Increased Risk of a House Fire
Finally, cheap solar glass puts your home at greater risk of a house fire. The PV cells under the glass conduct large amounts of electricity. If they become exposed — either because of glass expansion or physical damage — rain or snow contacting them could easily cause a fire.
High-quality glass that is impact-resistant and stable in extreme conditions will keep your home safe by maintaining a more permanent seal around the inner panel components.
The cost information presented in this article is derived from a comprehensive analysis, incorporating data from multiple industry sources. The average cost per watt per state was calculated based on figures from Consumer Affairs, Energy Sage, and Berkeley Lab’s Electricity Markets & Policy Department. Additionally, monthly energy consumption and the average monthly cost of electricity were sourced from the U.S. Energy Information Administration, ensuring a well-rounded and accurate representation of the information presented.
Related Solar Panel Guides
- What Are the Best Solar Panels for Hot Climates A Complete Homeowner’s Guide (2022)
- 10 Best Solar Panels for Homes in 2022 (Updated Solar Guide)
- Buyer’s Guide: Best Solar Panels for Camping (2022)
- 7 Best Solar Panels for Mobile Homes (2022 Guide)
- What Are the Best Solar Panels for Farming Solar for Agriculture Guide (2022)
- The Best Solar Panels for Portable Solar Generators
- Best Solar Panels for RV Solar Power System (2022)
Comparing authorized solar partners
-
- Industry-leading in-house financing
- Competitive pricing
- Excellent reputation
- Doesn't offer solar batteries (coming 2022)
A+Best Solar Financing2014Trina Solar, Canadian Solar, SolarEdge, Silfab, SunPower25-year manufacturer warranty; 10-year workmanship warranty, 2-year production guarantee
Having trouble deciding? Click below and use our process to receive multiple quotes instead:

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 







