10 Rivers Facing Pollution, Development, and Climate Change — And Policies That Can Help
An annual report highlights 10 waterways that have arrived at forks: where public support could determine whether they receive protection.

 Why you can trust us
Why you can trust us
Founded in 2005 as an Ohio-based environmental newspaper, EcoWatch is a digital platform dedicated to publishing quality, science-based content on environmental issues, causes, and solutions.
By Saima May Sidik
America’s waterways need help. Threats such as industrial pollution, poorly planned development, and climate change are widespread. In some cases, help could be imminent—but only with support from the public and lawmakers, according to a report out today from the conservation group American Rivers.
The report, called America’s Most Endangered Rivers, has been produced annually since 1984. Each report describes 10 threatened rivers, each facing an upcoming decision with the potential for public influence, such as whether to remove a dam or compel polluters to clean up waste.
Rather than a literal description of the rivers where the magnitude of threats is greatest, the document focuses on endangered rivers where “there’s something that people could actually do to really improve things there,” said Eve Vogel, a geographer from the University of Massachusetts Amherst who was not involved with the report but sometimes collaborates with American Rivers.
ㅤ
“There’s something that people could actually do to really improve things there.”
“I like the focus on action,” said hydrologist Reed Maxwell from Princeton University. He said he hopes the report will motivate the public to get involved with efforts to protect the threatened rivers listed in the report and with groups that advocate for the rivers in their own backyards.
New Threats Compound Old Problems
Climate change exacerbates problems that rivers have historically faced, such as dams, poorly planned development projects, and industrial pollution, said American Rivers vice president of communications Amy Souers Kober.
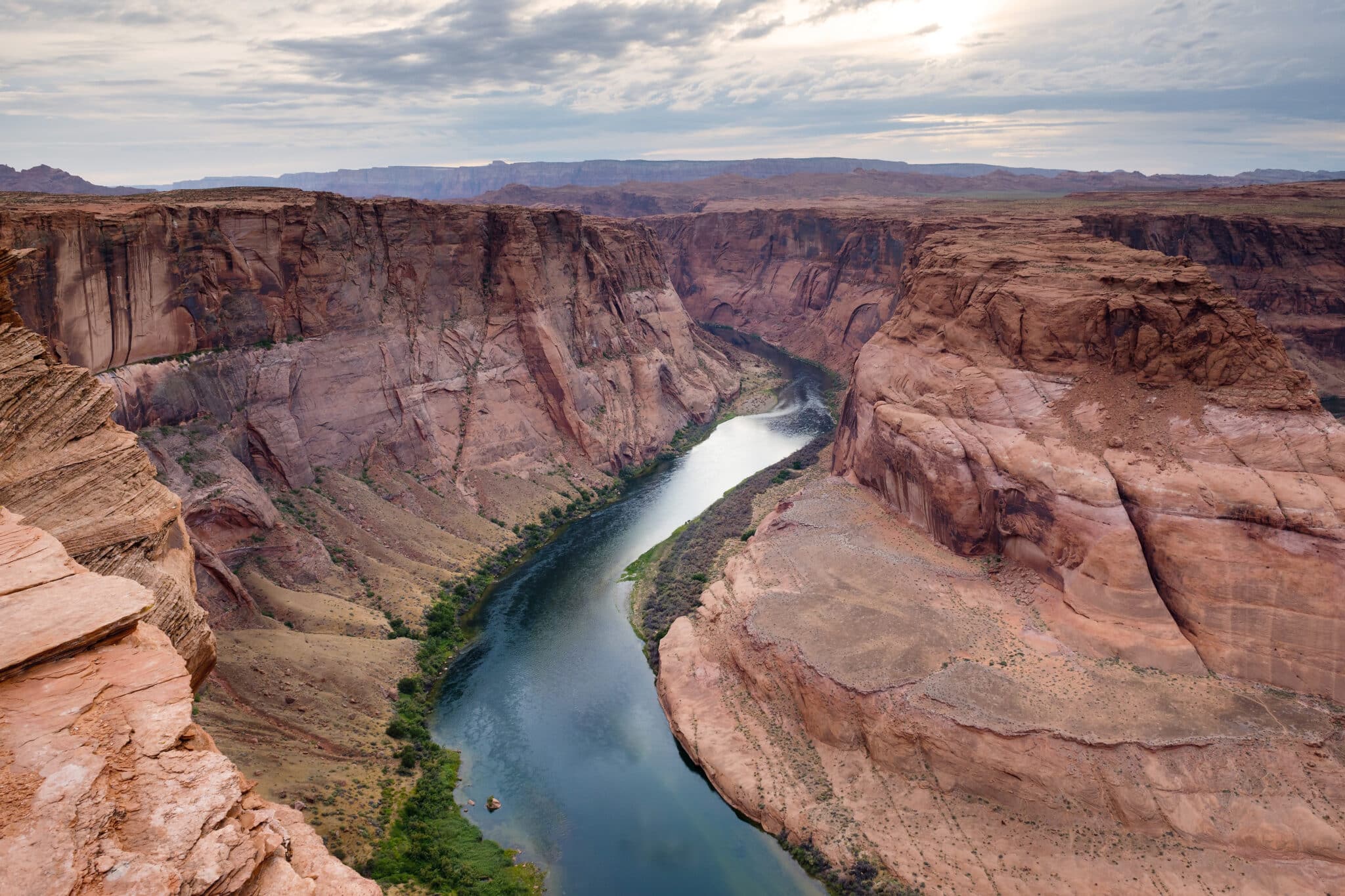
The Grand Canyon section of the Colorado River—number 1 on the list—is a prime example. The Colorado provides drinking water for 40 million people and irrigation for 5.5 million acres (2.2 million hectares) of farmland, as well as supporting 2,300 kilometers (1,450 miles) of river ecosystems. But as climate change has reduced precipitation along its banks, the water supply has dwindled, and the river has become overtaxed.
Without high flows that mobilize sand and sediment, sandbars within the Grand Canyon have eroded, damaging local ecosystems. Replicating the natural flow of water should be a priority so that this cultural icon doesn’t become an “ecological sacrifice zone,” according to the report. The U.S. Bureau of Reclamation has initiated a public comment period on their plans for how to manage the flow of water through the Grand Canyon, and American Rivers encourages the public to weigh in.
“Of course, there’s focus on protecting the Grand Canyon and how incredible it is, but the whole river should be protected in the same light.”
“Of course, there’s focus on protecting the Grand Canyon and how incredible it is,” said Daryl Vigil, a member of the Jicarilla Apache Nation and a cofacilitator of the Water & Tribes Initiative, “but the whole river should be protected in the same light.”
For the tribes in the Colorado basin, lack of water stymies attempts to develop sustainable economies and exacerbates inequities brought on by problems such as COVID-19, Vigil said.
Environmental regulations have helped curtail pollution over the past 50 years, but some rivers are in danger of sliding back toward problems of the past. For example, the Pearl River in Mississippi—number 3 on the list—is threatened by a private real estate development called the One Lake project. Planned dredging could disturb long-dormant industrial pollution on the riverbed, and dam construction could concentrate undertreated sewage in downstream communities. American Rivers is asking the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, the EPA, and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to reject the One Lake development.
“No one owns that river, and no one should be proprietary over who gets what water,” said Martha Watts, the mayor of Monticello, Miss.
On the American Rivers website, a description of each river is accompanied by an action button that makes it easy for the public to send emails to appropriate decisionmakers, encouraging them to protect rivers.
Joining or donating to a group that advocates for a local watershed is another way that the public can have a big impact on river health, said hydrogeologist Christine Hatch from the University of Massachusetts Amherst, who sometimes collaborates with American Rivers employees. Local groups can advocate for small changes that “if you tie them all together, can become bigger changes,” she said.
Widespread Issues—And Solutions
Endangered rivers can be found throughout the United States. Those highlighted in the report are as follows:
- Colorado River through the Grand Canyon (Arizona)
- Ohio River (Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia)
- Pearl River (Louisiana and Mississippi)
- Snake River (Idaho, Oregon, and Washington)
- Clark Fork River (Montana)
- Eel River (California)
- Lehigh River (Pennsylvania)
- Chilkat and Klehini Rivers (Alaska)
- Rio Gallinas (New Mexico)
- Okefenokee Swamp (Georgia)
Some of these rivers appeared on past lists. In other cases, rivers have been removed because their conditions have improved. The Boundary Waters in Minnesota, for example, appeared on last year’s list because it was threatened by a proposed mine. Actions taken by the Biden administration helped mitigate the risk. The annual endangered rivers list “plays a role in some of these big victories,” Souers Kober said.
This year, Souers Kober called out the Snake River in eastern Washington as one she’s keeping her eye on. Four federal dams have created reservoirs along what was once a free-flowing river. In these reservoirs, water temperatures often surpass what’s safe for salmon, which is one reason populations of this iconic fish are falling. Now, state and federal decisionmakers are looking for ways to replace the services the dams provide so that the dams can be removed. “It’s an exciting time right now because we’ve never been closer to getting to a solution,” Souers Kober said.
When rivers are poorly managed, often, communities of color and tribal nations are left bearing the brunt of the problems, and American Rivers has taken care to highlight the voices of people from these communities in the report.
“Who are we going to be in terms of this life-giving resource?”
Historically marginalized groups may be gaining a voice in water management, however. Over the past decade, water managers have become more willing to work with tribal nations to find equitable solutions to water problems, Vigil said. Several states have created Native American seats on the boards that govern use of the Colorado River, which is evidence of “huge steps in terms of the state acknowledging that parity of sovereignty,” he said.
These changes can’t come soon enough. Communities along the Colorado River have reached a “tipping point” when it comes to their relationships with water, Vigil said. Going forward, “who are we going to be in terms of this life-giving resource?” he asked.
Reposted with permission from EOS.
Subscribe to get exclusive updates in our daily newsletter!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy & to receive electronic communications from EcoWatch Media Group, which may include marketing promotions, advertisements and sponsored content.

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 



