The So-Called Political Divide on Coal vs. Renewables Is Fake News

By Jeff Turrentine
From a political standpoint, defending coal consumption is harder than ever. Coal is far and away the dirtiest fossil fuel there is in terms of carbon emissions and regular old air pollution (and its messy mining practices certainly aren’t helping its reputation). And when you factor in health care costs, environmental costs, and costs to local communities in the form of reduced tourism and property values, coal is also a real loser economically speaking—especially in relation to natural gas and renewables like wind and solar.
Still, lawmakers from coal-producing states and members of the current presidential administration have long attempted to justify their defense of coal on the grounds that it’s more than a fossil fuel: It’s a “way of life.” This has been a reasonably effective tactic, up to a point. If you’re trying to neutralize the arguments of those who want to see coal phased out of the U.S. energy diet, the best way to do so is to play the culture card: Point to all the people who rely on the coal industry for a regular paycheck and appeal to their sense of history and heritage.
But this last line of defense—”Renewables may be all the rage in San Francisco or Seattle or wherever, but where I come from, the people still love coal and always will”—may not be effective for much longer. Two recently released reports show how public sentiment regarding coal and renewables has shifted dramatically in recent years. One of them looks at attitudes at the national level; the other explores them in the historically coal-friendly state of Ohio. Both spell trouble for the future of an industry that’s already, by nearly all accounts, on its last legs.
Support/opposition for phasing out all coal-fueled power plants, fall 2017NSEE / University of Michigan and Muhlenberg College
The University of Michigan’s National Surveys on Energy and Environment (NSEE) is a biannual survey of public opinion surrounding issues of climate and energy policy, providing perhaps the best snapshot we could ever hope for in regard to how Americans stand on subjects like coal, renewables, climate science, geoengineering, a carbon tax and a host of other climate-related topics. Late last year, to commemorate its 10th anniversary of publication, NSEE released a trove of reports that illustrate just how much public opinion has changed on these matters over the past decade.
One of them in particular should strike fear into the hearts of the coal industry’s dead-enders and spark joy in the hearts of the rest of us. It shows that between 2016 and 2017, the number of Americans who strongly support a coal phaseout increased 11 percentage points, from 18 percent to 29 percent. In that same one-year period, the number of Americans who oppose a phaseout fell by the same amount. Remarkably, in states with active coal mines, strong support for a phaseout rose even more: by 13 points. Just as remarkably, this trend seemed to cut across political lines, rising among Democrats, independents and Republicans. Among the last group, strong support for a phaseout actually increased by 5 percentage points, whereas the number of Republicans who strongly oppose it fell by 14 points.
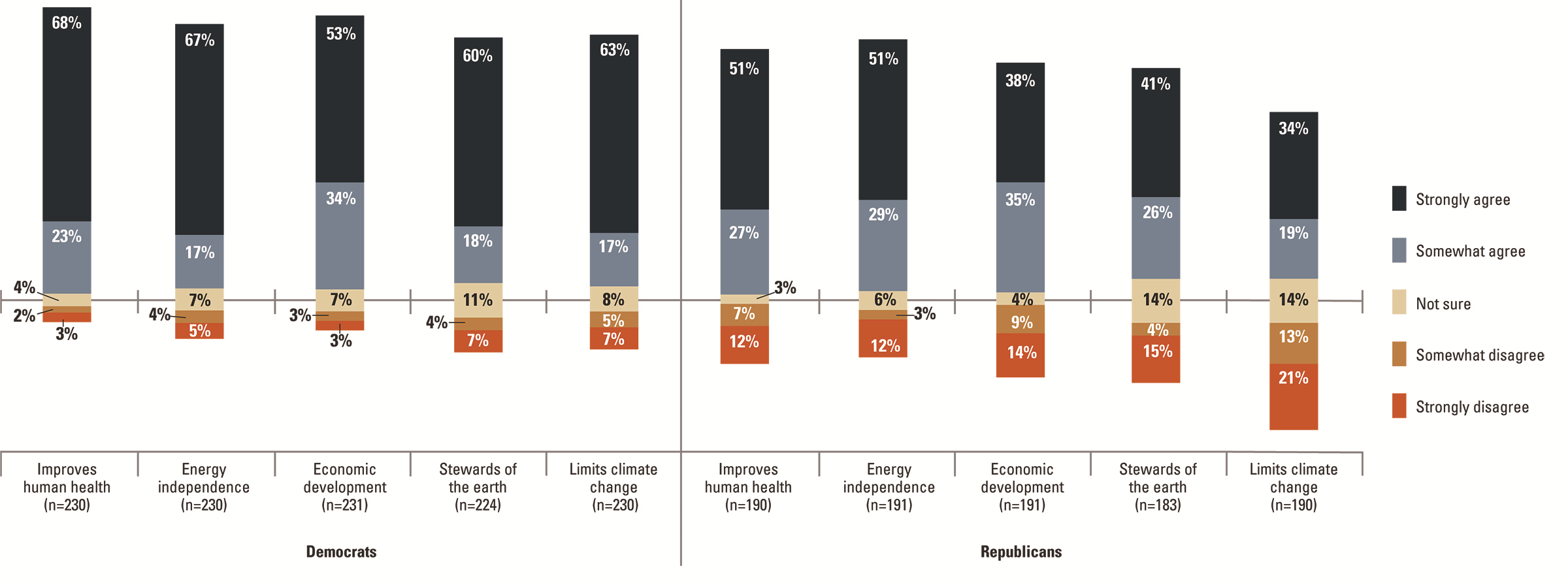
Agree/disagree on various potential benefits of renewable energyNSEE / University of Michigan and Muhlenberg College
Another NSEE report provides a perfect complement. As more Americans announce their willingness to say goodbye to coal, they’re also saying hello to the opportunity presented by renewables. This report reveals that 88 percent of Americans are in favor of increasing the use of solar energy in their state, and 82 percent feel the same about wind energy. Here, too, there’s real bipartisan buy-in, with 79 percent of self-identified Republicans getting behind solar and 72 percent getting behind wind. What’s more, the numbers show that a sizable majority of Republican, Democratic and independent respondents support requiring and/or subsidizing renewable energy production at the state level. Nearly two-thirds of Republicans surveyed—64 percent—said they like the idea of a state renewable energy requirement; even more amazingly, 65 percent of them said they have no problem with boosting the nascent renewables sector through subsidies.
[facebook https://www.facebook.com/nrdc.org/videos/2276253822386760/ expand=1]
But an even more eye-opening poll is making news too. An organization with a somewhat eyebrow-raising name, the Ohio Conservative Energy Forum, released the results of a survey last week suggesting that support for renewables is no longer a politically exploitable issue. In a survey of 400 Ohioans who self-identify as conservative, two-thirds of respondents said they believe their state needs to diversify its energy portfolio by having at least half of its energy come from renewable sources. Nearly the same percentage of respondents said they were more—not less—likely to support a politician who voted for or otherwise expressed support for renewable energy or energy efficiency legislation. Ohio, just as a reminder, currently ranks 11th in coal production among U.S. states, and its coal industry directly or indirectly supports about 33,000 jobs. It also ranks fourth among states in coal consumption.
For too long, it’s been too easy for lawmakers and administration officials to claim that by kowtowing to the coal industry’s wishes, they were simply doing right by voters. It’s getting harder. The gap between the interests of average Americans and the interests of coal-company executives is getting wider every day. And solar and wind are wedging their way in.
#Wind and #Solar Are the Final Nails in #Coal’s Coffin https://t.co/eVZpnIIUG2 @cleantechnica @BeyondCoal
— EcoWatch (@EcoWatch) January 14, 2019
Reposted with permission from our media associate onEarth.

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe