
The Built Environment and Fashion Industries Are Primed to Lead the Recovery

A woman is seen shopping in a boutique. Thomas Barwick / Getty Images
By Amol Mehra
Set against rising calls for action to combat growing inequality and the climate crisis, the COVID-19 pandemic underscores the importance of the key drivers of industry and economic reform: workers, communities and the environment.
The crisis has laid bare the perils of relying on purely market-based approaches. This should not be a surprise to those who have long railed against the free market, shareholder-centric approach, derived from current neoliberal economic narratives.
The tide is turning, however, and business leaders are starting to understand that their legitimacy may hinge on how they respond. Those who seize this moment will surely benefit from the swing in momentum towards a more human and environment-centered approach to doing business.
Take for example the calls to “Build Back Better” from the “We Mean Business Coalition” – a group of over 1000 companies with a market cap of over trillion who are organizing to support climate action and just economy approaches.
Through setting commitments for companies and building collective power to lobby governments and policy-makers, this group is joining the chorus of human rights, labour and environmental movements which have been ringing the alarm for change for some time. Together, the approach has huge potential to shift the debate – and to lead to meaningful action on the part of policy-makers to commit to tackling the threats posed by the climate crisis.
These two industries – the built environment and fashion – are sectors that are ripe for transformation and where even subtle shifts have potential for wide-reaching transformation. Here’s why:
The Built Environment
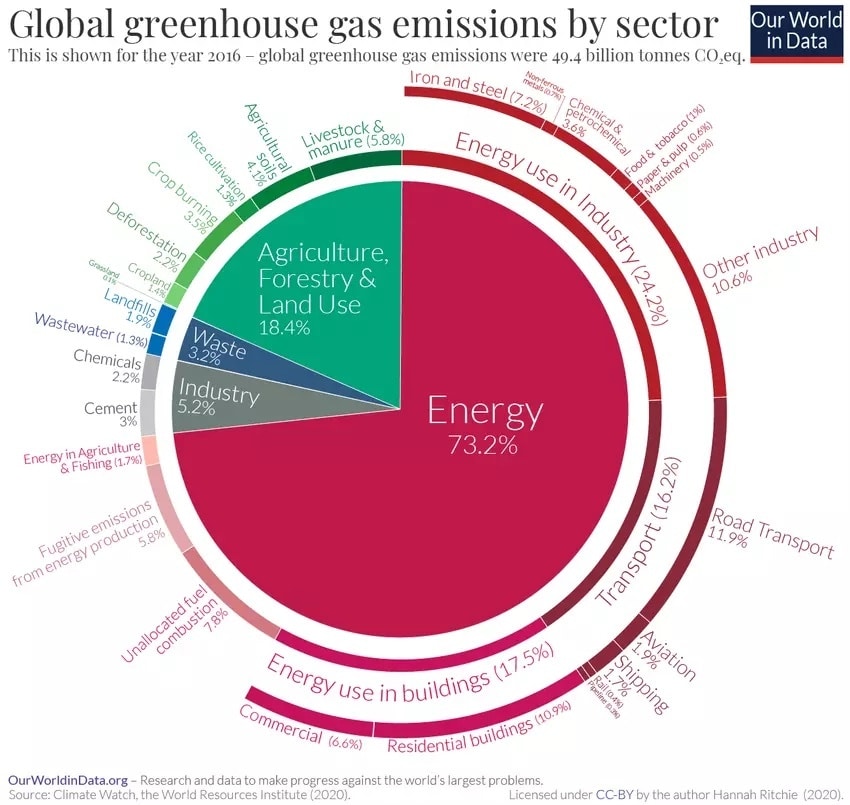
The built environment – the physical places and structures that we inhabit – is a huge potential change agent in this regard. Buildings and construction account for massive amounts of energy usage and about 40% of global CO2 emissions, providing a clear pathway to shift current consumption and production pathways.
The construction sector accounts for around 13% of the world’s GDP and for 7.2% of the global workforce. Many of the jobs linked to these sector have a negative history of labour rights, especially with respect to migrant laborers. As experts have noted, the scale of the industry and its relative impacts on labour markets and the environment make it a prime agent of transformation of the broader global economy.
By prioritizing approaches that focus on decarbonization and the promotion of labor rights protections, we can create economic opportunities that promote healthy, regenerative structures. Efforts are starting to seed in this regard, with increased attention being placed to mass timber and other wood products in construction, as well as the use of natural materials in buildings.
At the same time, leading human rights organizations are looking more closely at promoting rights-based approaches.
Not all industries are equal. ourworldindata.org
Fashion
But this isn’t the only sector with transformative power. The fashion sector produces nearly 10% of the world’s carbon emissions and is the second largest consumer of the water, all while employing between 60 and 70 million workers in garment supply chains.
While there have been laudable innovations in recent years towards adopting circularity and increasing the use of organic materials, there is still huge potential to promote transformative change in protections for workers.
Workers in the sector are often left without social protections, exposing them to vulnerability. In recognition of this need, the International Labor Organization, business actors and labor rights leaders have committed to take action to protect garment workers’ income, health and employment, and to work together to establish sustainable systems of social protection for a more just and resilient garment industry.
This “Call to Action” launched in April 2020 and now needs steady implementation. The effort should seek to cast a wide tent, bringing in other industry players and leveraging development actors as well.
What’s clear from the examples above is that critical, much needed efforts are starting to emerge and that these efforts need to be encouraged and accelerated. As social movements, consumers, investors, regulators and businesses themselves start to realize the value of transforming practices, the momentum will increase for other sectors to follow suit. This domino effect will spur the economic transformation that is so desperately needed to ensure that the environment, and the people who inhabit it, can live in a healthy, just society.
There can be no doubt: transformation of our economic system is imperative. The moment is now for businesses, and the industries they are part of, to seize it.
Reposted with permission from World Economic Forum.

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 