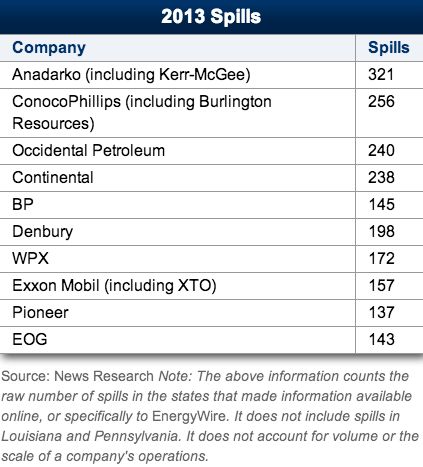
The rate of oil drilling in the U.S. leveled off in 2013, but the same can’t be said for the amount of spills that took place.
According to a report from E&E Publishing, there were at least 7,662 spills, blowouts, leaks and similar incidents last year in 15 of the top states for onshore oil and gas activity. In states where the publication could compare results for both years, the publication determined there were about 20 more spills per day than in 2012.
While most of the spills were small, they amounted to more than 26 million gallons of oil, fracking wastewater and more. That’s equivalent to the amount of oil BP gushed into the Gulf of Mexico in 2010.
No all-encompassing list of U.S. oil spills exist, so E&E had to analyze results from different states. The trouble there is that not all states keep track and some simply didn’t make good on the publication’s request for data. For instance, Mike Soraghan writes that Louisiana referred E&E to the U.S. Coast Guard’s National Response Center, but the database is shut down. The group also did not respond to a Freedom of Information Act request from March.
North Dakota, Montana Pennsylvania and Texas were among the states with the largest increases. Production-related spills more than doubled to 103 in Ohio, but that figure is tiny compared to other states.
“We still have this mentality that we have to go faster and faster,” said Don Morrison of the Dakota Resource Council, an environmental group that monitors activity in the Bakken formation. “When you’re rushing, things go wrong.”
In some states, the spill increases have led to more enforcement, while that’s not the case in others. Notices of alleged violations increased by 50 percent in Colorado. Since 2010, the Ohio Department of Natural Resources tripled the number of workers who deal with oil and gas to more than 100. That includes 50 inspectors.
In Texas, officials issued one-third more noncompliance shutdown threats than in 2012. However, an agency spokeswoman told E&E that most of that bump arose from delinquent reports. The actual number of enforcement penalties that were assessed dropped by 40 percent.
In addition to the analysis, Soraghan got a commitment from Continental Resources Inc., the largest operator in the Bakken formation, to reduce spills, maintain spill prevention teams and take “appropriate action” against contractors who don’t make an improvement. Examples include steel-lined containment systems and emergency shutdown systems at well sites.
“All these enhancements are part of our drive to continuously improve,” said Tom Oddie, vice president of health, safety, security and environment for Continental.
——–
YOU ALSO MIGHT LIKE
About 10,000 Gallons of Crude Oil Spills onto Los Angeles Area Streets
Chicago Mayor Demands Answers From BP After Oil Spill
Ohio Pipeline Spill Leaked Double the Amount of Crude Oil Originally Estimated
——–

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe