
Why I Ride My Bike to Work, by the Prime Minister of the Netherlands

Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte commuting by bicycle. Evert-Jan Daniels / AFP / Getty Images
By Kate Whiting, David Knowles
With its sweeping views over the sparkling Hofvijver pond, the Binnenhof — the Gothic castle in the heart of The Hague that houses the States General of the Netherlands — is quite something.
It’s little wonder Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte enjoys commuting to his office there. And recently he’s made the journey by bike as often as possible.
“I didn’t cycle a lot for 10 years. But for the past two years, I’ve had my own bike again and, when the weather allows, I travel into the office that way,” he told the World Economic Forum.
Cycling Craze
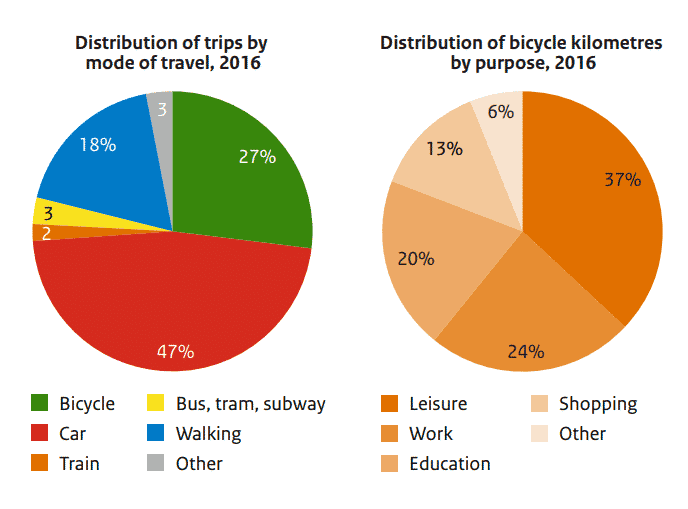
More than a quarter of trips in the Netherlands 2016 were made by bike.
Netherlands Institute for Transport Policy Analysis
The Dutch are famous for their love of cycling. In 2018, the country had more bicycles than people: 23 million to 17 million. More than a quarter of all trips in the country are made by bike and of those, a quarter are for getting work, like Rutte.
He explains why it’s long been such a phenomenon: “The Dutch love cycling because we are a small country. We have to get from A to B. And of course taking a car, yes, is an option, but you have congestion plus the environmental impact. From the old days, almost from the late 19th century, we’re used to taking a bicycle.”
Enabled by Infrastructure
The country’s flat landscape is perfect for trips on two wheels. But it has also carefully designed its transport infrastructure to promote cycling.
There are more than 35,000 kilometers (21,750 miles) of cycle lanes and the city of Utrecht is home to the world’s biggest underground bike park.
Rutte admits he was impressed with how well-oiled the system is: “I was amazed how many specific biking traffic lights and biking lanes we now have – and so many more than 10 years ago.
“They’re not only in the city but also in local communities between cities, which makes it very safe and easy, particularly for small children when they go to school.”
Healthy for People and Planet
Why the Netherlands is so good at cycling, according to its prime ministerThe country has more bicycles than people.➡️ ecowatch.com/mark-rutte-bikes-to-work
Posted by EcoWatch on Thursday, September 26, 2019
The health benefits of cycling are well-known: it reduces the risk of illnesses such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, and can help boost mental wellbeing.
A 2015 study found more than 6,000 deaths in the Netherlands are prevented each year due to cycling, and it adds six months to the average life expectancy.
This saves the country’s economy more than million a year.
The benefits to the environment are also huge: switching from a car to a bicycle saves an average of 150 grammes of carbon dioxide per kilometre, according to the Netherlands Institute for Transport Policy Analysis.
As Rutte says: “The whole system is nudging people to make use of this very healthy alternative.”
Note: This article is part of the Sustainable Development Impact Summit.
Reposted with permission from our media associate World Economic Forum.
- Netherlands Launches Landmark Zero-Subsidy Wind Power Auction ...
- The Netherlands Can Feed the World. Here's Why It Shouldn't ...

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 