
From Dining Pods to See-Through Masks: 6 Helpful Inventions During the Pandemic
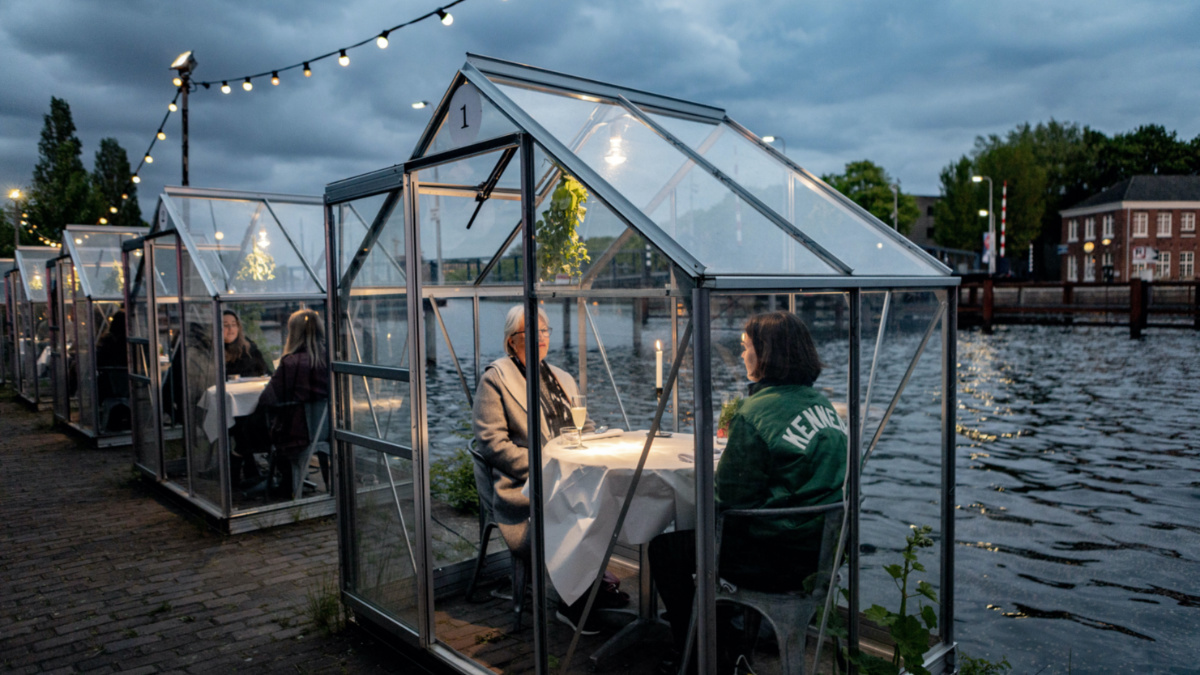

An Amsterdam restaurant uses greenhouses to protect against the coronavirus on May 12, 2020 in Amsterdam, Netherlands. Paco Nunez / Anadolu Agency / Getty Images
By Harry Kretchmer
It’s more than five months since Wuhan, the city where the coronavirus outbreak began, went into lockdown marking the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions.
In that time, there have been many innovative ideas to help us live with the virus and return to work and leisure safely.
The World Economic Forum’s crowdsourcing platform UpLink is looking for the best solutions around the world to tackle today’s most pressing issues.
Here are six areas of everyday life where inventions are easing the challenges posed by the pandemic.
1. Dining Out
At the height of the lockdown, retail analysts, Kantar, studied social media for clues about what people were most looking forward to doing when lockdowns were eased. The top three desires included eating out and going to a bar with friends.
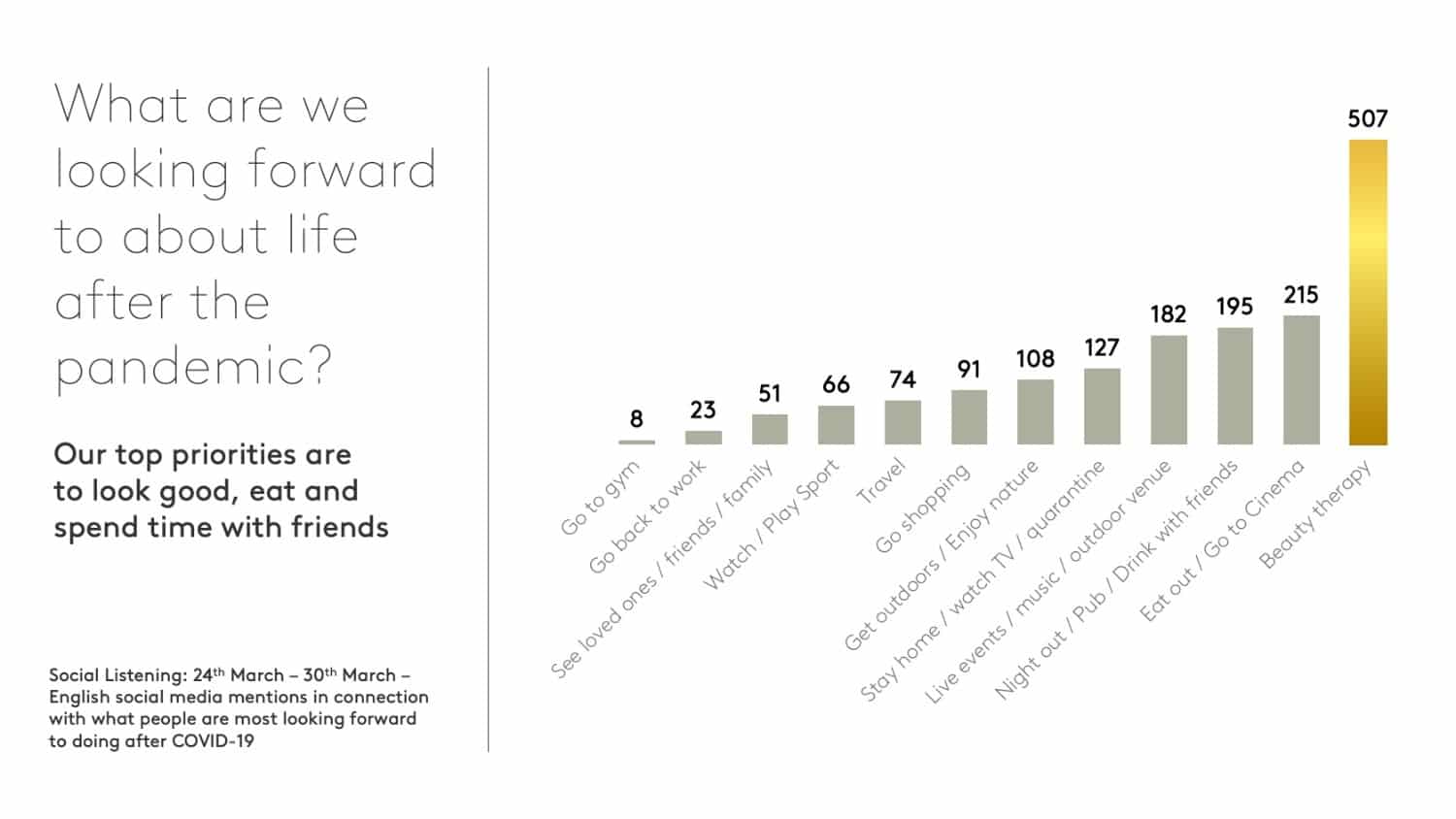
Social activities are top of people’s wish lists after lockdown. Kantar
But with social distancing measures in place for such businesses, attention has turned to how to keep customers safe and inspire trust.
French designer Christophe Gernigon has created oversized transparent lampshades, allowing diners to eat in a personal bubble. The ‘PLEX’EAT’ prototypes are made from perspex.
In the Netherlands, Amsterdam’s ETEN restaurant has also been making dining safer. On the banks of a canal it has installed glass houses to protect dining companions, and help with social distancing.
Meanwhile in South Korea, popular watering holes are devising more hi-tech ways to protect patrons: robot bartenders.
One – named ‘Cabo’ can carve a perfect spherical ice ball for whisky ‘on the rocks.’ Another can measure out cocktail liquor from 25 bottles hanging from the ceiling.
2. Shopping
Grocery shopping boomed during the pandemic, with much of the growth coming from online – a service relied on by many of those shielding from the virus.
But many of those most at risk from COVID-19 are still wary of coming into stores, in part because of the possibility of the virus living on surfaces which are frequently touched – like the handle on a fridge door.
A Finnish supermarket created an innovative solution – long, curved handles that allow customers to open chiller cabinets with their clothed arms instead of hands.
3. Communicating
Masks are mandatory – and essential – in many settings, especially on public transport and in shops. However, for those who are deaf, they can cause a real problem: they cover lips, making it impossible to lip-read.
This was the experience of a deaf tailor from Indonesia who faced a daily struggle with new regulations mandating mask wearing in public places.
Her solution is brilliantly simple: she has created masks with a clear plastic window over the mouth – making it possible to lip-read once again.
Another communication innovation takes the form of a robot. ‘Pepper’ is a humanoid robot who can be found at a Tokyo hotel. But it is no ordinary hotel: its patients are those who have mild coronavirus symptoms.
Pepper’s job is to greet patients as they arrive – making them feel welcome, but also protecting – and freeing up – staff.
4. Cleaning
Some of the most creative solutions have come from the world of robotics.
Refugees at the Za’atari refugee camp in Jordan have developed a LEGO robot that automatically dispenses hand sanitizer – reducing the risk of infection.
Elsewhere, robots are cleaning all kinds of surfaces. Meet “Ugo,” the remote-controlled robot developed by Japanese start-up Mira Robotics.
It uses ultraviolet light to kill viruses, and can patrol buildings and clean on its own.
5. Home Deliveries
"We definitely see this trend continuing with more and more people embracing delivery robots. Not everybody wants to necessarily spend time running errands."https://t.co/g5qsMnPeyL
— Starship Technologies (@StarshipRobots) June 22, 2020
Around the world, robots are being enlisted to help with deliveries of food.
U.S. start-up Starship Technologies is rolling out its food delivery boxes on wheels to a range of urban areas, from Milton Keynes, England to Fairfax, Virginia.
Colombian start-up Rappi is another company whose boxy wheeled robots have moved onto the pavements in greater numbers during the pandemic.
6. Social Distancing
At the heart of most nations’ public health strategies to fight COVID-19 is effective social distancing. But sometimes people need to be reminded. Singapore has chosen a robot for this task.
Made by U.S. company Boston Dynamics, ‘Spot’ patrols the park and reminds visitors to maintain social distancing: “Let’s keep Singapore healthy. For your own safety, and for those around you, please stand at least one meter apart. Thank you.”
Reposted with permission from World Economic Forum.

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 