Indigenous Australians Take Fight Against Giant Coal Mine to the United Nations

By Noni Austin
For tens of thousands of years, the Wangan and Jagalingou people have lived in the flat arid lands of central Queensland, Australia. But now they are fighting for their very existence. Earlier this month, they took their fight to the United Nations after years of Australia’s failure to protect their fundamental human rights.
A company called Adani Mining Pty Ltd, part of the Adani Group of companies founded by an Indian billionaire named Gautam Adani, is determined to build the massive Carmichael Coal Mine and Rail Project on the Wangan and Jagalingou’s ancestral homelands. If built, the Carmichael Coal Mine would be among the largest coal mines in the world, with six open-cut pits and five underground mines, as well as associated infrastructure like rail lines, waste rock dumps and an airstrip.
Coals mine are immensely destructive: The Carmichael mine would permanently destroy vast areas of the Wangan and Jagalingou’s ancestral homelands and waters, and everything on and in them—sacred sites, totems, plants and animals. It would also likely destroy the Wangan and Jagalingou’s most sacred site, Doongmabulla Springs, an oasis in the midst of a dry land. The development of the mine would also result in the permanent extinguishment under Australian law of the Wangan and Jagalingou’s rights in a part of their ancestral homelands.
The Wangan and Jagalingou’s lands and waters embody their culture and are the living source of their customs, laws and spiritual beliefs. Their spiritual ancestors—including the Mundunjudra (Rainbow Serpent), who travelled through Doongmabulla Springs to shape the land—live on their lands.
Wangan and Jagalingou traditional lands.Wangan and Jagalingou
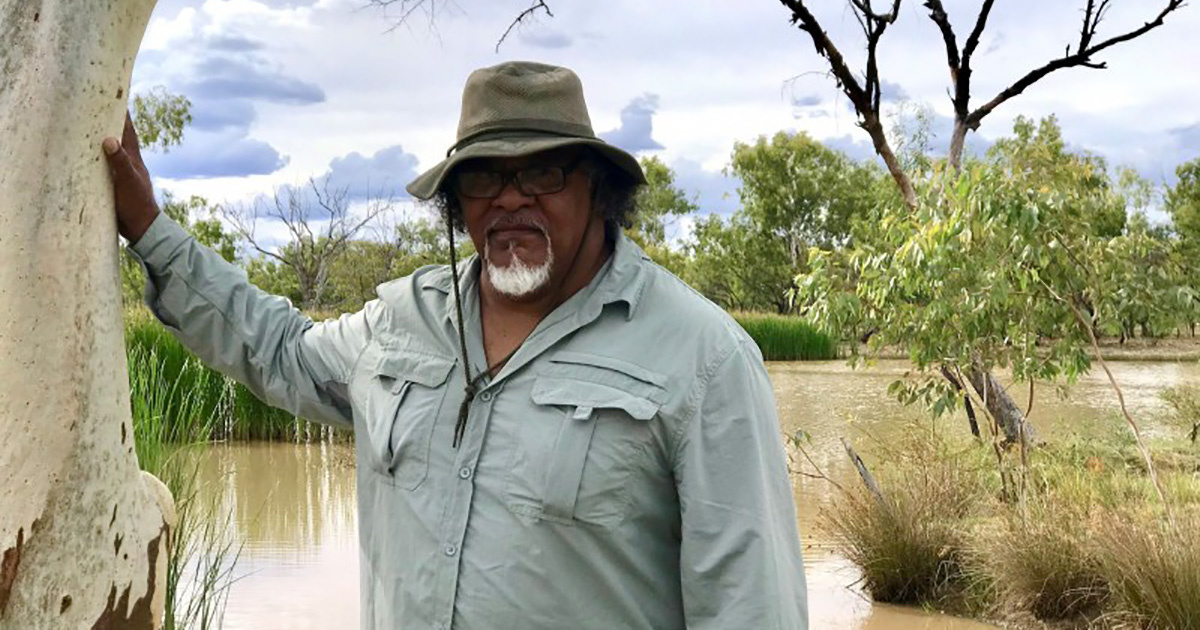
As Wangan and Jagalingou authorized spokesperson and cultural leader Adrian Burragubba said, “Our land is our life. It is the place we come from, and it is who we are. Plants, animals and waterholes all have a special place in our land and culture and are connected to it.”
Consequently, the destruction of the Wangan and Jagalingou’s lands and waters is the destruction of their culture. If their lands are destroyed, they will be unable to pass their culture on to their children and grandchildren, and their identity as Wangan and Jagalingou will be erased.
Murrawah Johnson, authorised youth spokesperson of the Wangan and Jagalingou, said, “In our tribe, women teach our stories to our young people. I want my children and their children to know who they are. And if this mine proceeds and destroys our land and waters, and with it our culture, our future generations will not know who they are. Our people and our culture have survived for thousands of years, and I cannot allow the Carmichael mine to destroy us. I will not allow myself to be the link in the chain that breaks.”
The Wangan and Jagalingou have consistently and vehemently opposed the Carmichael mine, rejecting an agreement with Adani Mining on four occasions since 2012. Throughout its dealings with the Wangan and Jagalingou, Adani Mining has used the coercive power of Australian legislation and acted in bad faith, holding fraudulent meetings and manipulating the Wangan and Jagalingou’s internal decision-making processes.
In these circumstances, the development of the Carmichael mine violates the Wangan and Jagalingou’s internationally protected human rights, including the right to continue practicing their culture and to use and control their ancestral homelands, as well as the right to be consulted in good faith and to give or withhold their consent to mining projects on their lands.
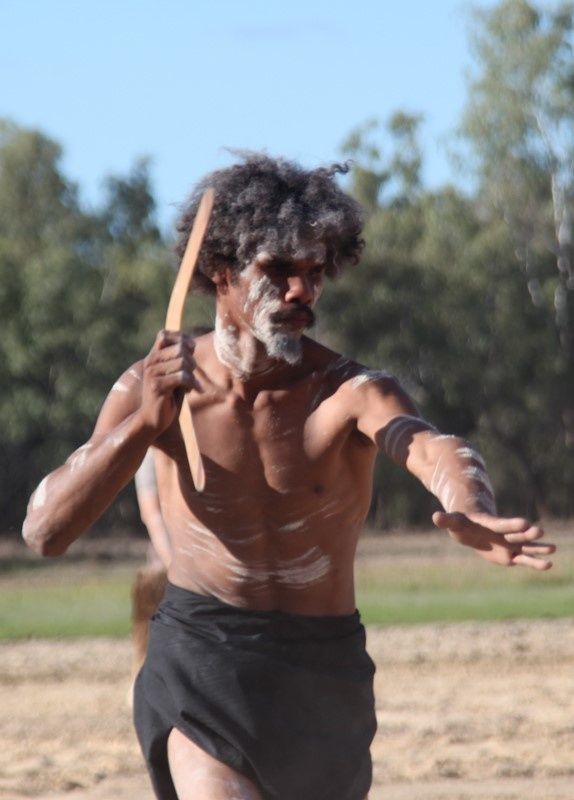
A man participates in a ceremonial dance on Wangan and Jagalingou ancestral lands.Wangan and Jagalingou
Despite the Wangan and Jagalingou’s persistent objections and their pleas to the Australian and Queensland governments to protect their human rights, both governments have approved the mine and publicly support it, and Adani Mining remains steadfastly determined to develop the project as soon as possible. The Wangan and Jagalingou have also brought litigation in Australia to protect their homelands, but have been unsuccessful to date because Australian law allows private companies and the government to override the Wangan and Jagalingou’s rights in their ancestral lands.
Now, to protect their fundamental human rights, the Wangan and Jagalingou have been forced to seek help from a United Nations human rights watchdog. Recently, the Wangan and Jagalingou asked the UN Committee on the Elimination of Racial Discrimination to urgently ensure Australia protects their homelands and culture. The committee is the enforcement body of the UN Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination, a treaty Australia has signed. The convention is one of the core international treaties among the world’s nations that protect our most basic human rights, including Indigenous peoples’ rights to culture and land.
If Australia will not listen to its own people, the Wangan and Jagalingou hope it will listen to international community and cease prioritizing the profits of a foreign company over the permanent loss of a people who have been connected to the land since time immemorial.
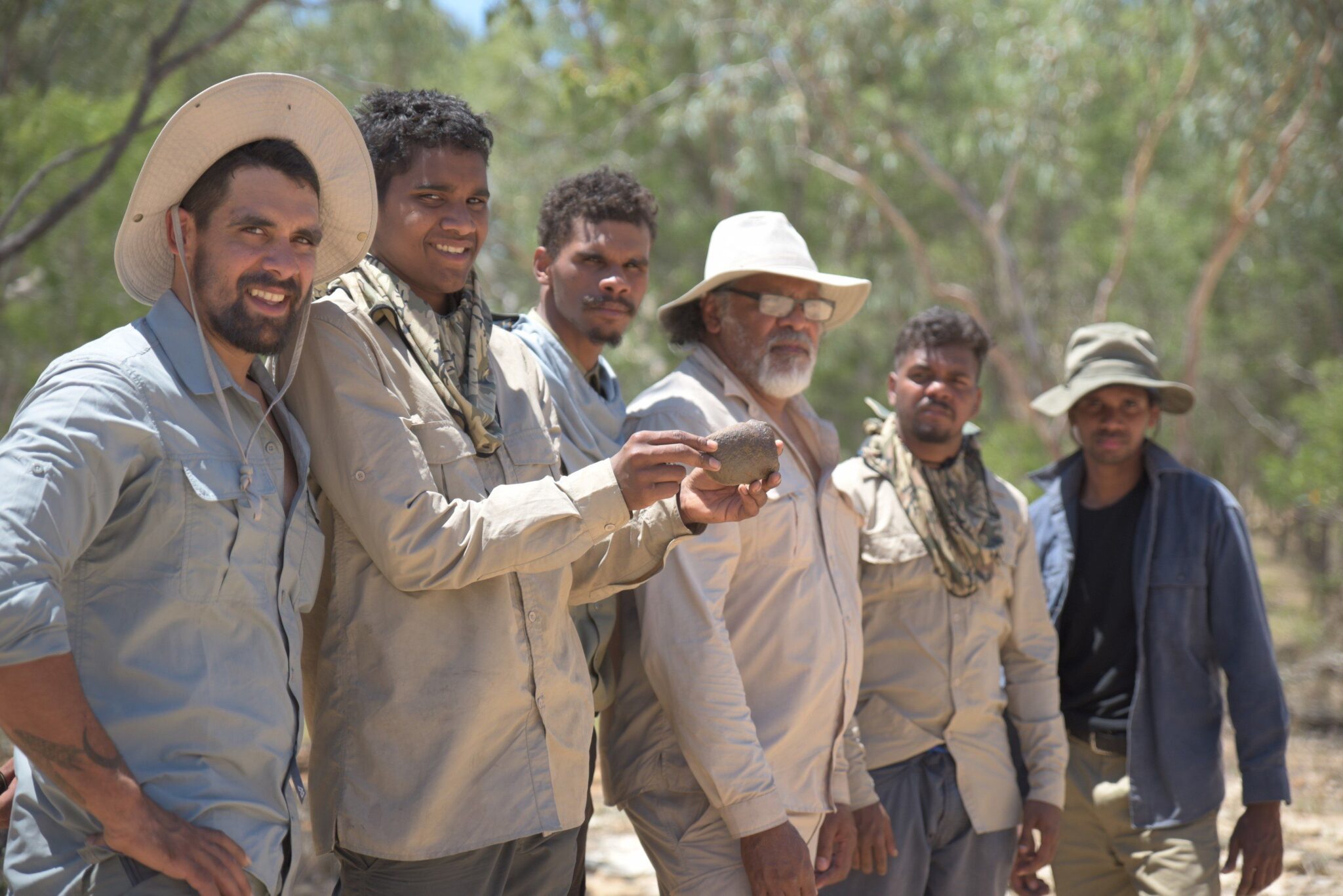
Adrian Burragubba provides cultural teachings to Wangan and Jagalingou young men on their ancestral lands. Wangan and Jagalingou
Earthjustice assisted the Wangan and Jagalingou to prepare their request for urgent action to the UN.

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe