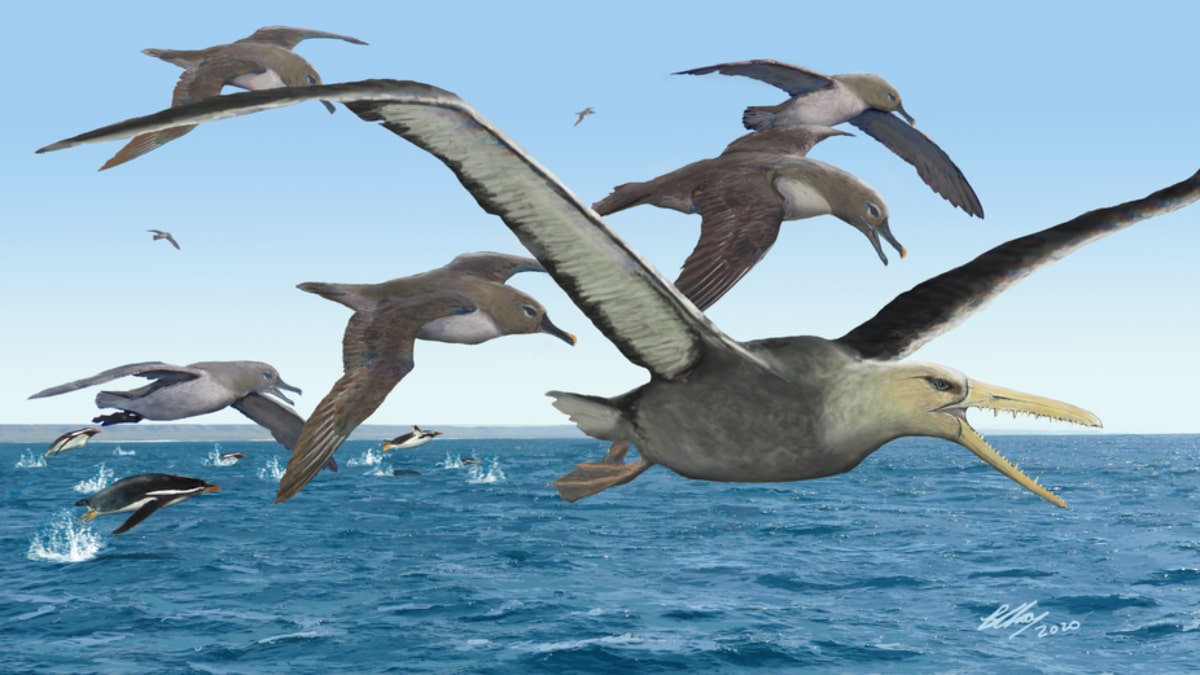


Fossil remains indicate these birds had a wingspan of over 20 feet. Brian Choo, CC BY-NC-SA
By Peter A. Kloess
Picture Antarctica today and what comes to mind? Large ice floes bobbing in the Southern Ocean? Maybe a remote outpost populated with scientists from around the world? Or perhaps colonies of penguins puttering amid vast open tracts of snow?
Fossils from Seymour Island, just off the Antarctic Peninsula, are painting a very different picture of what Antarctica looked like 40 to 50 million years ago – a time when the ecosystem was lusher and more diverse. Fossils of frogs and plants such as ferns and conifers indicate Seymour Island was much warmer and less icy, while fossil remains from marsupials and distant relatives of armadillos and anteaters hint at the previous connections between Antarctica and other continents in the Southern Hemisphere.
There were also birds. Penguins were present then, as they are now, but fossil relatives of ducks, falcons and albatrosses have also been found in Antarctica. My colleagues and I have recently published an article revealing new information about the fossil group that would have dwarfed all the other birds on Seymour Island: the pelagornithids, or “bony-toothed” birds.
Giants of the Sky
As their name suggests, these ancient birds had sharp, bony spikes protruding from sawlike jaws. Resembling teeth, these spikes would have helped them catch squid or fish. We also studied another remarkable feature of the pelagornithids – their imposing size.
The largest flying bird alive today is the wandering albatross, which has a wingspan that reaches 11 ½ feet. The Antarctic pelagornithids fossils we studied have a wingspan nearly double that – about 21 feet across. If you tipped a two-story building on its side, that’s about 20 feet.
Across Earth’s history, very few groups of vertebrates have achieved powered flight – and only two reached truly giant sizes: birds and a group of reptiles called pterosaurs.
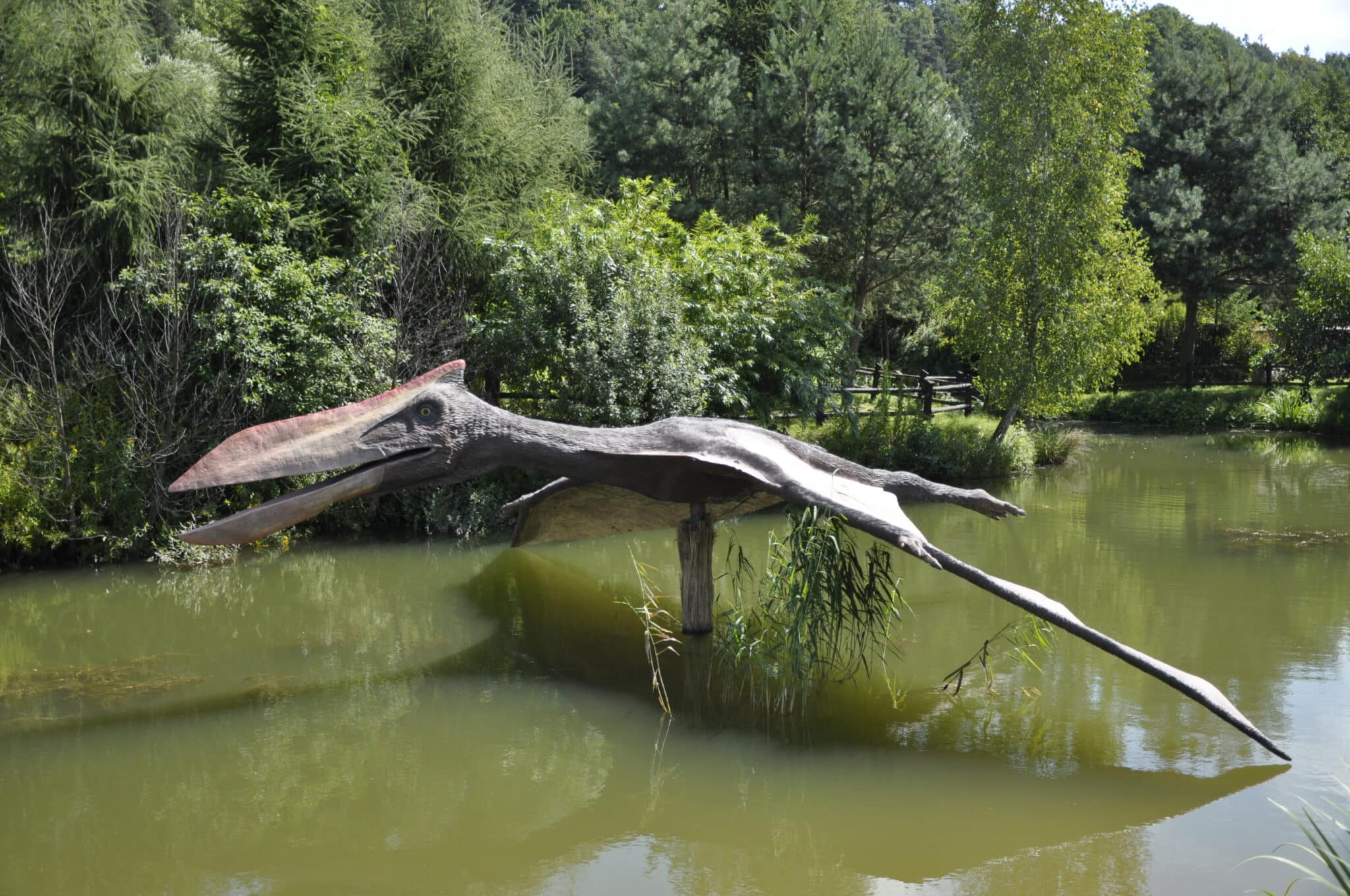

Full-size model of a Quetzalcoatlus on display at JuraPark in Baltow, Poland. Aneta Leszkiewicz / Wikimedia
Pterosaurs ruled the skies during the Mesozoic Era (252 million to 66 million years ago), the same period that dinosaurs roamed the planet, and they reached hard-to-believe dimensions. Quetzalcoatlus stood 16 feet tall and had a colossal 33-foot wingspan.
Birds Get Their Opportunity
Birds originated while dinosaurs and pterosaurs were still roaming the planet. But when an asteroid struck the Yucatan Peninsula 66 million years ago, dinosaurs and pterosaurs both perished. Some select birds survived, though. These survivors diversified into the thousands of bird species alive today. Pelagornithids evolved in the period right after dinosaur and pterosaur extinction, when competition for food was lessened.
The earliest pelagornithid remains, recovered from 62-million-year-old sediments in New Zealand, were about the size of modern gulls. The first giant pelagornithids, the ones in our study, took flight over Antarctica about 10 million years later, in a period called the Eocene Epoch (56 million to 33.9 million years ago). In addition to these specimens, fossilized remains from other pelagornithids have been found on every continent.
Pelagornithids lasted for about 60 million years before going extinct just before the Pleistocene Epoch (2.5 million to 11,700 years ago). No one knows exactly why, though, because few fossil records have been recovered from the period at the end of their reign. Some paleontologists cite climate change as a possible factor.
Piecing it Together
The fossils we studied are fragments of whole bones collected by paleontologists from the University of California at Riverside in the 1980s. In 2003, the specimens were transferred to Berkeley, where they now reside in the University of California Museum of Paleontology.
There isn’t enough material from Antarctica to rebuild an entire skeleton, but by comparing the fossil fragments with similar elements from more complete individuals, we were able to assess their size.
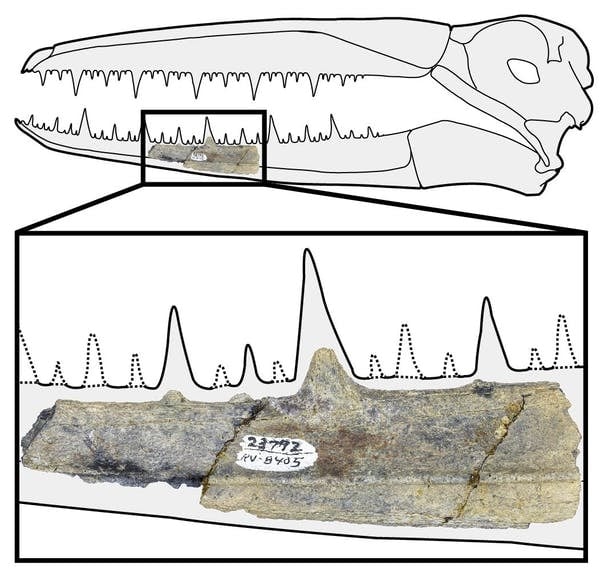
In life, the pelagornithid would have had numerous ‘teeth,’ making it a formidable predator. Peter Kloess, CC BY-NC-SA
We estimate the pelagornithid’s skull would have been about 2 feet long. A fragment of one bird’s lower jaw preserves some of the “pseudoteeth” that would have each measured up to an inch tall. The spacing of those “teeth” and other measurements of the jaw show this fragment came from an individual as big as, if not bigger than, the largest known pelagornithids.
Further evidence of the size of these Antarctic birds comes from a second pelagornithid fossil, from a different location on Seymour Island. A section of a foot bone, called a tarsometatarsus, is the largest specimen known for the entire extinct group.
These pelagornithid fossil findings emphasize the importance of natural history collections. Successful field expeditions result in a wealth of material brought back to a museum or repository – but the time required to prepare, study and publish on fossils means these institutions typically hold many more specimens than they can display. Important discoveries can be made by collecting specimens on expeditions in remote locations, no doubt. But equally important discoveries can be made by simply processing the backlog of specimens already on hand.
Peter A. Kloess is a Doctoral Candidate, Integrative Biology, University of California, Berkeley.
Disclosure statement: Peter A. Kloess does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Reposted with permission from The Conversation.
- Climate Change Threatens Two-Thirds of North American Bird ...
- 37% of North American Birds Face Extinction - EcoWatch
- Meet Five 'Extinct' Species That Have Returned to Life - EcoWatch
- New Dinosaur Fossils Could Belong to Largest Creature to Walk on Earth - EcoWatch

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 