
110 Million Americans May Be Drinking PFAS-Contaminated Water

More than 1,500 drinking water systems across the country may be contaminated with the nonstick chemicals PFOA and PFOS, and similar fluorine-based chemicals, a new EWG analysis shows. This groundbreaking finding comes the same day the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is convening a summit to address PFAS chemicals—a class of toxic chemicals that includes PFOA and PFOS, and that are linked to cancer, thyroid disease, weakened immunity and other health problems.
From 2013 to 2015, the EPA mandated national testing for PFAS chemicals in public water systems, yet the full results of this testing, funded by taxpayers, were never made public. Water utilities with the highest concentrations of PFAS chemicals have been publicly identified. But the names of utilities with detectable PFAS contamination below the so-called reporting levels of 10 to 90 parts per trillion, or ppt, were not released. Millions of people were not informed that their water supply is contaminated with these chemicals.
The additional water systems with PFAS contamination likely serve tens of millions of people, and it is essential for people in those communities to be informed of this hazard. Eurofins Eaton Analytical, which analyzed a third of the nationwide water samples, found that 28 percent of the water utilities it tested contained PFAS chemicals at concentrations at or above 5 ppt. The percentage of samples with PFAS detections nearly doubled when the laboratory analyzed down to 2.5 ppt. Based on this data, EWG’s analysis suggests that up to 110 million Americans could have PFAS in their water.
This new research greatly exceeds EWG’s previous estimate of 16 million Americans being exposed to PFAS-contaminated water, as reported in the EWG’s national Tap Water Database.
Independent scientific assessments find that the safe level of exposure to PFAS chemicals is about 1 ppt—significantly below the reporting level set by the EPA.
Just over a week ago, InsideEPA and Politico broke news that the White House and the EPA attempted to bury a proposal from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry that suggested exposure to Teflon and Scotchgard chemicals may be harmful at levels 10 times lower than what the EPA has publicly called safe. The full ATSDR proposal has not been made public, but the available information indicates the lower level was proposed because ATSDR accounted for harm to the immune system. This mirrors the more health protective approach New Jersey took in drafting its drinking water limits of 13 ppt for PFOS and 14 ppt for PFOA.
The full implications a lower safe exposure level would have are uncertain because the extent of national drinking water contamination is unknown. The uncertainty is largely due to the reporting value the EPA has previously used. PFAS detections below the reporting limits were kept secret, and may have never been recorded.
Today’s EPA summit on the PFAS contamination crisis carries no indication that the agency will take action. In fact, the public might expect the opposite result, given internal EPA emails showing that top aides to Administrator Scott Pruitt and White House officials attempted to suppress the ATSDR proposal, worrying that release of the study would be “a public relations nightmare” for the Trump administration.
EWG calls on the EPA, testing laboratories and drinking water utilities across that country that have PFAS testing results to make the information public immediately. Knowing the locations and extent of contamination is critical for cleaning up water supplies and making the case for regulation.
Secret PFAS Contamination Data
In the water testing mandated by the EPA under the third Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule, or UCMR, 198 different water utilities had recorded detections of PFAS chemicals in amounts above the EPA reporting limit. But the reporting limits were very high, using 40 ppt for PFOS and 20 ppt for PFOA, though many labs have much more sensitive detection limits. Some analytical labs are able to detect amounts as small 2 ppt of PFAS chemicals in water.
Based on a reanalysis of the national dataset by Eurofins Eaton Analytical, a water testing lab that processed more than 30 percent of nationwide water samples, EWG estimated how many utilities would likely have contaminated water if the reporting values had been set lower. At a reporting limit of 5 ppt, an estimated 1,046 utilities could have tested positive. If all results down to 2.5 ppt were reported, we estimate that over 1,900 of the 4,920 water utilities tested in the U.S. would have reported contamination.
Using maps generated by Eurofins Eaton Analytical and the public UCMR results, we calculated the number of water utilities that the lab identified as having PFOA or PFOS in their water, without results being reported to the EPA. Some states such as New Jersey have done additional water testing and have likely identified some, if not all, of the utilities that have PFAS chemicals in their water.
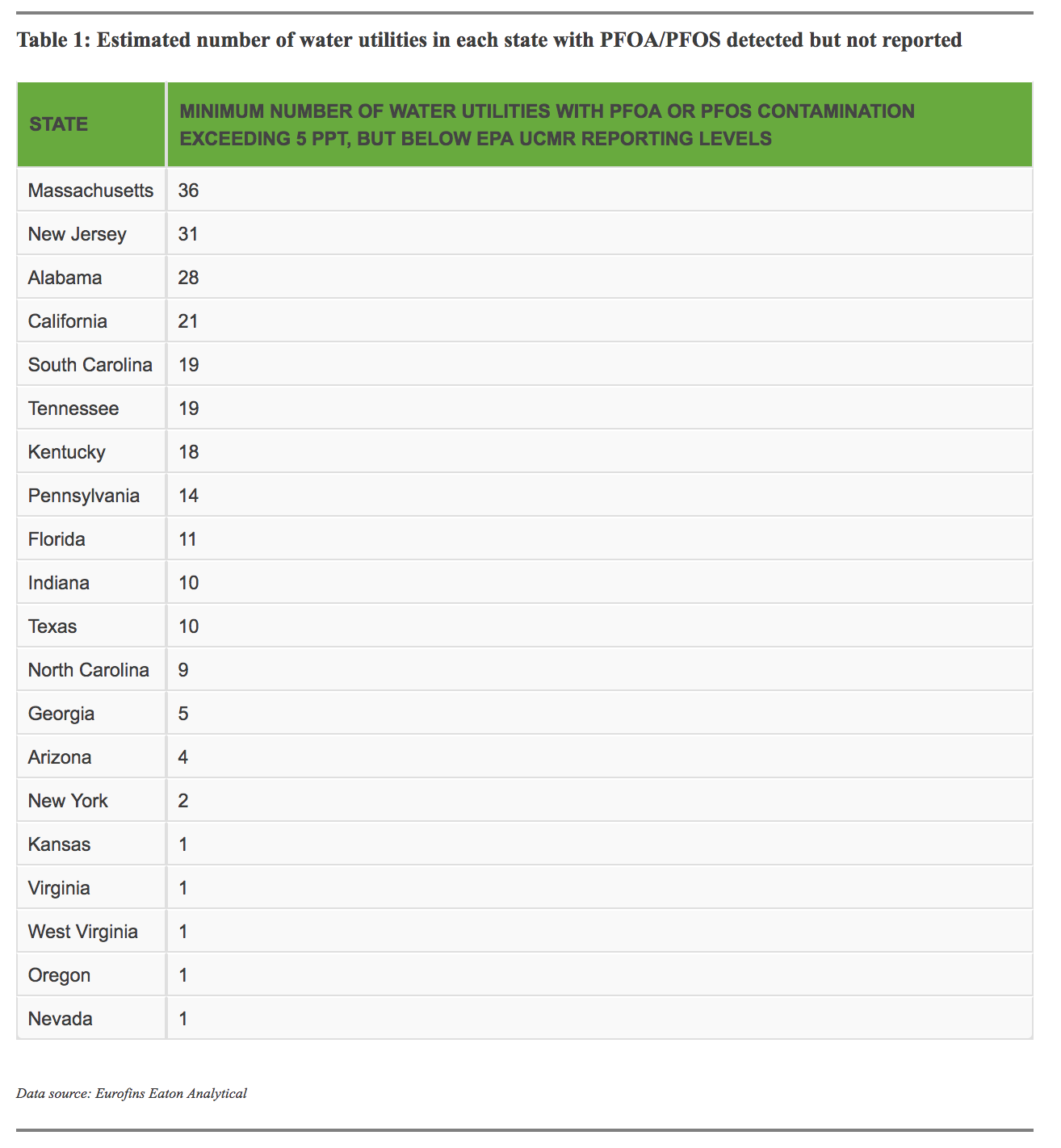
The PFAS water contamination issue is not going away and the EPA needs to take immediate action to both understand the full extent of contamination and ensure Americans have safe drinking water.
EWG Methodology for Estimating Number of Public Water Systems With Possible PFAS Contamination
In Eurofins Eaton Analytical presentations in 2017, the laboratory indicated that it had analyzed water samples from 1,800 water utilities and had measured PFAS concentrations that were much lower than those reported by the EPA. The lab reported 5.3 percent of water samples tested positive for PFAS chemicals at the UCMR limits, compared to 4.02 percent of samples from all laboratories that analyzed UCMR samples. Eurofins Eaton Analytical also found that 28 percent of all water systems had PFAS levels above 5 ppt, and 42 percent of all water samples had PFAS chemical concentrations at or above 2.5 ppt.
Based on the sensitive results from Eurofins Eaton Analytical, we estimated the number of American water systems with PFAS levels at or above 2.5 and 5 ppt. To calculate the number of utilities estimated to have detections at 5 ppt, we used the ratio of detections between Eurofins lab at UCMR levels and at 5 ppt compared with the overall detection ratio for all labs at UCMR levels. We estimate that 21.3 percent of water utilities in the UCMR program would likely have PFAS detections at 5 ppt or higher, and the detection frequency approximately doubles when comparing levels of 5 ppt and 2.5 ppt.

If 39 percent of the U.S. population was exposed to PFAS chemicals, this would represent approximately 127 million people, and 39 percent of the population served by water systems tested in the UCMR program would represent approximately 90 million people.
An alternative way to estimate the number of people affected by PFAS contamination is to compare the ratio of the 4 percent of utilities that tested positive in the UCMR program, representing 16 million people, to our estimate of 39 percent of water systems that have PFAS levels of 2.5 ppt or greater. This yields an estimate of 117 million people with PFAS in their water at levels at or above 2.5 ppt.
On average, these three estimates indicate that 110 million people could have PFAS chemicals in their water at levels of 2.5 ppt or higher.
Interactive Map Shows If Your Tap Water Is Contaminated With PFCs https://t.co/y3g8rOP29K @ewg @foodandwater @Water @charitywater
— EcoWatch (@EcoWatch) June 15, 2017

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 