
Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon Increases for 13th Consecutive Month

Aerial picture showing a deforested piece of land in the Amazon rainforest in northern Brazil on August 23, 2019. Carl de Souza / AFP / Getty Images
by Rhett A. Butler
Despite the global economic slowdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic, deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon appears to be continuing largely unabated with forest clearing over the past 12 months reaching the highest level since monthly data started being released publicly in 2007, according to official data released Friday by the country’s national space research institute INPE. Forest loss in Earth’s largest rainforest has now risen 13 consecutive months relative to year-earlier figures.

INPE’s deforestation monitoring system, DETER, detected 406 square kilometers of forest loss in the “legal Amazon” during the month of April. That brings the extent of deforestation measured by the system to 9,320 square kilometers for the year ended April 30, 2020, 40% higher than where it stood a year ago and more than twice as high as it was in April 2018.
5,606 square kilometers of forest have been lost since the “deforestation year” began August 1, 2019, the highest on record for this time of year.
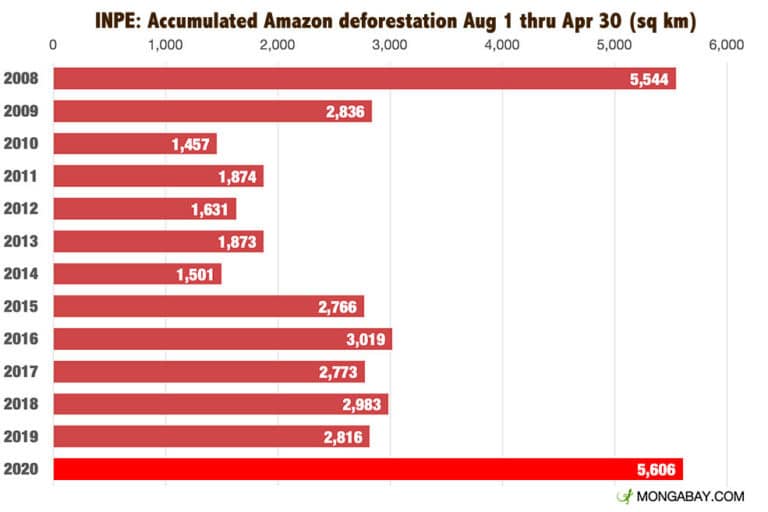
Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon, which accounts for nearly two-thirds of the Amazon rainforest, has been trending upward since bottoming at 4,571 square kilometers in 2012. Prior to that, deforestation had been declining in the region thanks to better forest monitoring and environmental law enforcement, public and private sector efforts to curb forest clearing, the creation of new protected areas and indigenous territories.
According to a 2014 study published in the journal Science, the drop in deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon between 2004 and 2013 avoided the greenhouse gas emissions equivalent of taking all cars off American roads for three years — 3.2 billion tons.
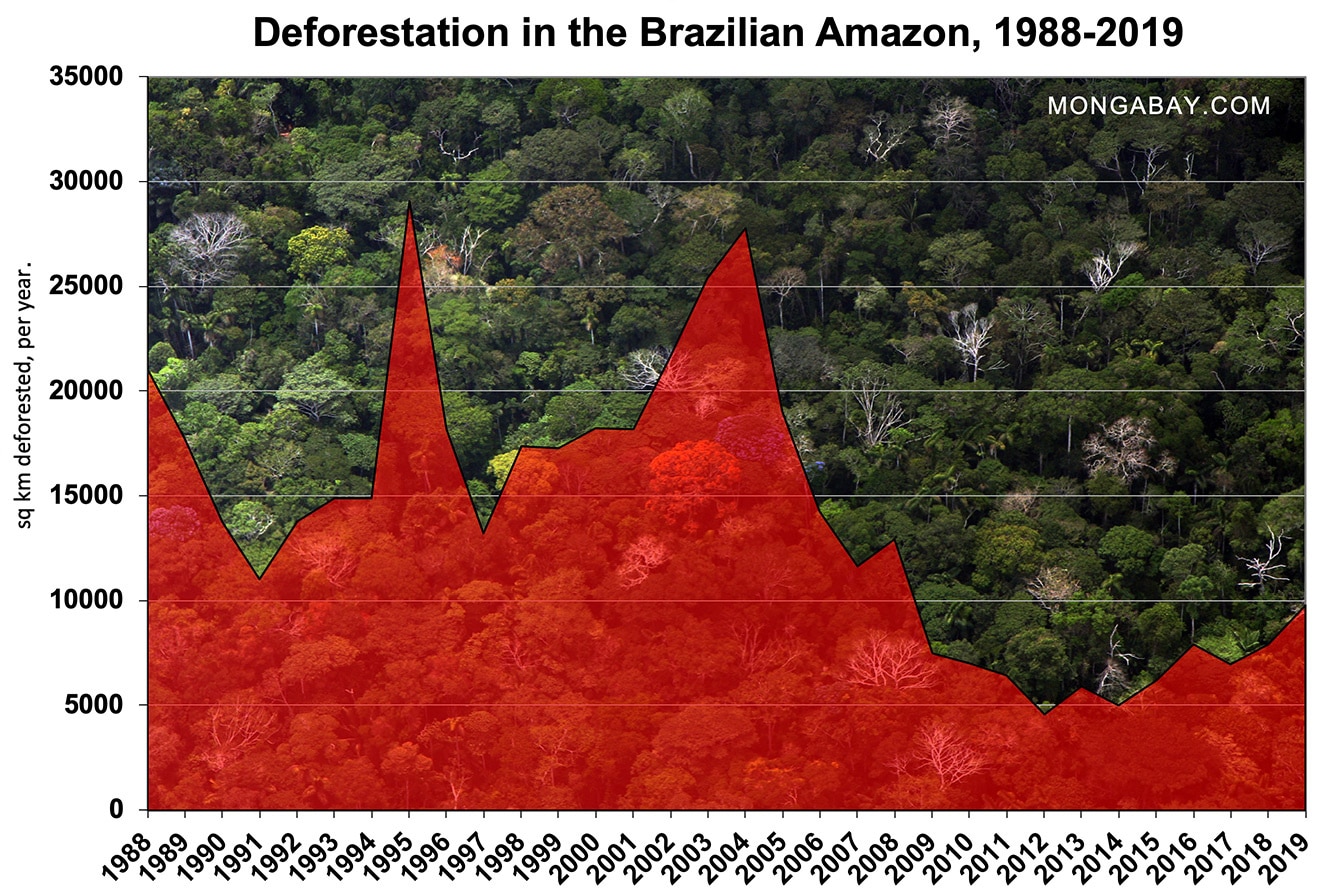
Official Brazilian government data showing annual deforestation (Aug 1-Jul 31 year) in the Brazilian Amazon since 1988.
The rise in deforestation has been particularly sharp since Jair Bolsonaro assumed the presidency in January 2019. Bolsonaro has rolled back environmental regulations, granted amnesty from fines for illegal deforestation, cut budgets for environmental law enforcement, diminished the role of scientists in the government, blamed environmental NGOs for deforestation and claimed without evidence that Leonardo DiCaprio funded last year’s fires in the Amazon, and opened protected areas and prospective indigenous territories for extractive industries and agribusiness. He’s openly called for more deforestation in the Amazon, while his administration has sacked officials charged with protecting forests and indigenous peoples against illegal land invasions.

Amazon rainforest canopy in Brazil. Rhett A. Butler / Mongabay
The combination of rising forest clearance and abnormally dry conditions across vast swathes of Brazil is setting up the region for an active fire season. Last year, fires in the Amazon made international headlines when the resulting smoke billowed over Sao Paulo, blocking out the sun mid-day. Widespread condemnation from NGOs, human rights groups, business leaders, celebrities, and European political leaders as well as global calls for boycotts of Brazilian companies and products prompted Bolsonaro to mobilize the army to help with fire-fighting efforts. Yet Bolsonaro pressed forward with policies and actions that will increase deforestation and fires nonetheless, say experts.
Accelerating deforestation, forest degradation, and drought in the Amazon is of great concern to scientists who warn that the entire biome may be near a tipping point where large areas of wet rainforest could transition to dry tropical woodlands and savanna. Such a transition could have dramatic implications for regional rainfall, with the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone potentially shifting northward, leading to drier conditions across South America’s breadbasket and major urban areas. The impact on regional economies could be substantial, while the impact on ecosystem function and biodiversity of the Amazon could be devastating, according to researchers.
Reposted with permission from Mongabay.
- Amazon Rainforest Reaches Point of No Return - EcoWatch
- Brazil's Amazon Rainforest Is the Wild West for Illegal Gold Miners ...
- Brazil Using Pandemic as Smokescreen for New Attacks on the ...
- New Study: China and EU Soy Imports Are Increasing Brazil's Deforestation
- Study: Amazon Droughts Can Be Predicted in Advance - EcoWatch
- Deforestation in Amazon Skyrockets to 12-Year High Under Bolsonaro - EcoWatch
- Study Warns of Severe Drying in Amazon Rainforest
- Deforestation in Brazilian Amazon Accelerates to Highest Level in 15 Years - EcoWatch

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 