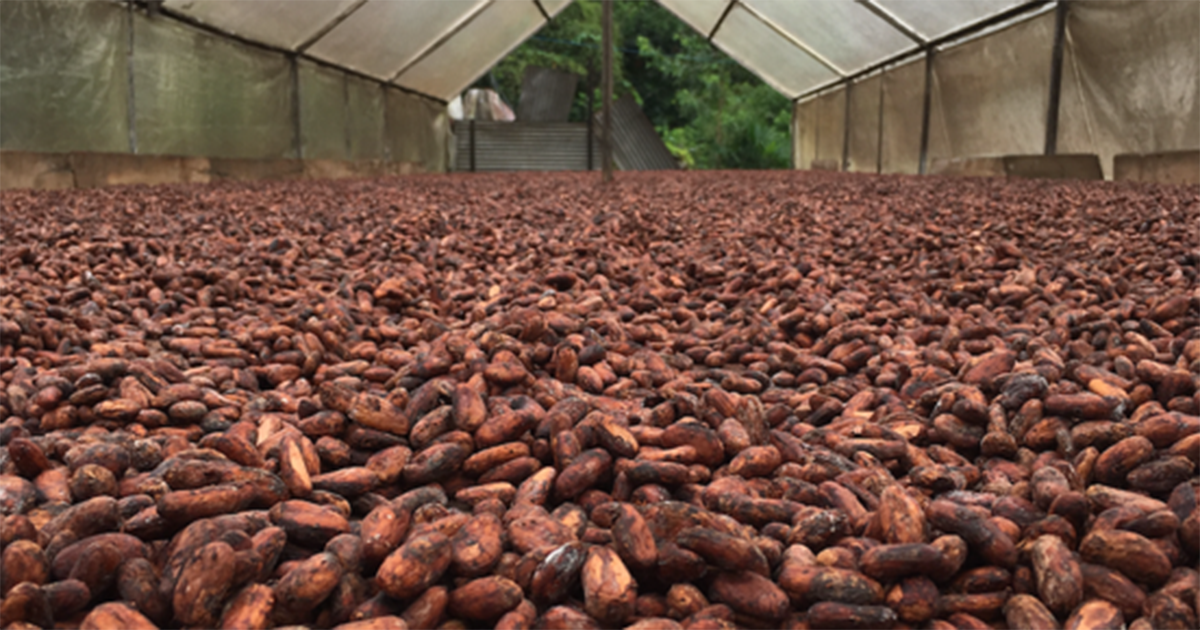


Picture this: a world where chocolate is as rare as gold. No more five-dollar bags of candy on Halloween. No more boxes of truffles on Valentine’s day. No more roasting s’mores by the campfire. No more hot chocolate on a cold winter’s day.
Who wants to live in a world like that?
Unfortunately, we all could be if our climate keeps changing.
So how will the climate crisis affect one of the world’s most beloved culinary delights? The verdict doesn’t look good for chocolate lovers worldwide — and more importantly, it’s a threat to the farming communities that depend on cacao for their livelihoods.
Cacao is in Trouble
Cacao, or the cocoa bean, is the main ingredient in chocolate. A rather picky plant, it grows only in the warm, humid regions near the equator, largely in areas designated as rainforests. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, cacao trees require steady temperatures, high humidity, lots of rain, nitrogen-rich soil, and protection from wind to thrive.
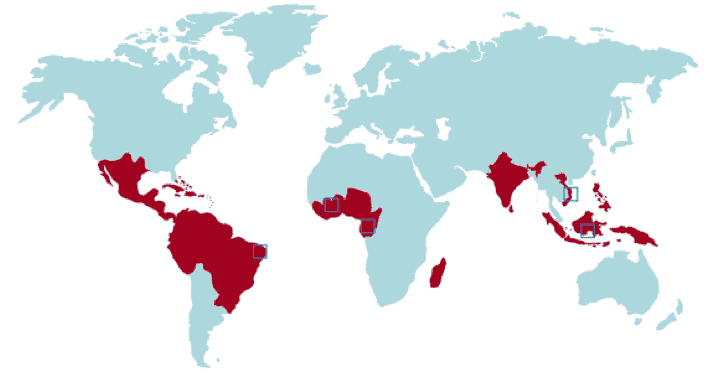
Cacao is grown in the regions highlighted in red below:
The climate crisis is already affecting many of the world’s crops, including another fan favorite: coffee. Unlike coffee, which suffers most from rising temperatures, cacao is impacted most by decreased humidity. Regions where cacao grows best often have humidity levels of 100 percent during the day and 70–80 percent at night.
One major (and often under-discussed) facet of the climate crisis is its impact on the water cycle. As the globe heats up, the stages of the water cycle become more erratic and floods and droughts become more prevalent and extreme. In tropical environments, rising temperatures lead to increased evaporation rates and decreased humidity, causing cacao crops to suffer.
A 2013 report found that the land area suitable for the cultivation of cacao is shifting dramatically. The optimal growing altitude in Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire, which combined produce over 50 percent of the world’s cacao, is expected to rise between 800 and 1,150 feet by 2050.
As suitable growing conditions are pushed uphill, some plots of land will have to be abandoned entirely, and others are likely to experience a dramatic drop in crop yields.
Impacts on Cacao Farmers

The cooperative employs direct trade practices, in which they purchase cacao directly from the local Kichwa people.
The Kichwa remain true to the traditional farming techniques practiced by their ancestors. They grow cacao in chakras, or jungle gardens, that incorporate the tree into the existing rainforest. The result is a decadent variety of all-natural cacao, with no deforestation necessary.
Kallari farmers must now travel deeper into the jungle to harvest their plants. This fact – coupled with changing weather conditions making it more difficult to grow cacao in the first place – puts entire communities like the Kallari farmers at risk.

Kallari generates a portion of its revenue from the sale of chocolate bars, but relies mostly on contracts with European distributors for large quantities of wholesale cacao. Without the ability to provide the best price for the cacao, distributors are quick to turn to other sources.
It’s not hard to imagine what could come next. Entire regions could be left without any competitive advantage in the (very competitive) global market. Some cacao farmers may even be forced to clear rainforest land to farm other crops. Which would destroy natural habitats and add carbon to the atmosphere, all while losing precious farming traditions in the process.
Many farming families — whose money is already spread very thin — rely on cacao sales as their only source of income. The Fair Trade Foundation, a global leader in workers’ rights, states, “ninety percent of the world’s cocoa is grown on small family farms by about six million farmers who earn their living from growing and selling cocoa beans.”
Chocoholics Beware
All that said, we know what you’re thinking, “How will I get my chocolate fix in 2050?” The answer is that you might not at all.
In an interview with the Independent, John Mason of the Nature Conservation Research Centre said, “In 20 years, chocolate will be like caviar. It will become so rare and so expensive that the average Joe just won’t be able to afford it.”
This has many chocolatiers predicting that while chocolate won’t necessarily go away entirely, the market may shift from cheaper, more-accessible candies like Hershey bars and Cadbury eggs toward more luxurious chocolates.
Chocoholics: get ready to pay top dollar for what’s left of the world’s chocolate come 2050 – or perhaps even sooner.
Adapting: The Future of Chocolate

So how can we avoid this chocopocalypse?
Farmers in the Bahia region of Brazil have come up with an innovative solution: the Cacao Cabruca Agroforestry system.
Under this system, cacao trees are planted in the shade of other trees, protecting them from sun, wind, and pests. This technique has been used since the early nineteenth century, but has experienced a surge in popularity due to the rapidly changing climate. In some regions, farmers transplant trees solely for the purpose of providing shade for their cacao.
This system also provides another benefit: it averts deforestation, maintaining the nutrient content of the soil and absorbing and storing carbon from the atmosphere.
But innovation doesn’t stop in Brazil. Farmers in Indonesia are working closely with the Rainforest Alliance to implement practices like this as part of a broader commitment to climate-smart agriculture, or CSA. Climate-smart agriculture is an umbrella term for a variety of agricultural practices, all designed to combat the climate crisis while preserving farms. Some of these include replacing synthetic fertilizers with organic compost, planting cover crops to improve soil health, digging trenches to control erosion, and using natural pesticides.
And the good news is that embracing CSA isn’t just good for the planet as a whole – it can also be good for individual famers and their crops. Sustainable techniques that focus on soil health have been shown to improve crop yields as well as plant resilience to numerous climate change impacts.
Meanwhile, back in Ecuador at Kallari Association, tourists can visit el vivero, or the plant nursery, which features an experimental plot of different varieties of cacao. The goal is to find a variety that can withstand warmer, drier conditions.
We know that big problems require big solutions.
Farmers and scientists around the world are putting the most innovative practices in sustainable agriculture to work in the field. But if we’re going to save the world’s culinary treasures, we must all work together to stop this crisis. Bold, swift action on climate will ensure that many generations to come can enjoy the creamy delight of a chocolate bar.
Take Action
Want to take action on the climate crisis and do your part to protect the world’s chocolate supply and the farmers who provide it? We’re here to help.
The Climate Reality Project works around the globe to raise awareness of the climate crisis and inspire bold action in communities everywhere. Get involved in your local community by joining one of our local chapters or sign up for our email list to find out how you can fight the climate crisis and protect the world’s culinary delights!

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe 